How Manufacturing 4.0 Got Its Name—and Why It Matters

Flashback to 2015: “Hamilton” debuted on Broadway, millennials surpassed baby boomers as the largest U.S. generation and the term “Industry 4.0” was gaining traction in manufacturing circles. It was also when the Manufacturing Leadership Council created a conceptual framework called “Manufacturing 4.0.”
So what is the difference between Industry 4.0 and Manufacturing 4.0? While the terms may not sound all that distinct from each other, Manufacturing 4.0 represents the MLC’s commitment to a far-sighted, holistic approach to manufacturing’s tech-enabled metamorphosis—one that has served it well in over the past eight years.
The background: The 4.0 movement started in Germany in 2011 when the German ministries for education, research, economic affairs and energy developed a strategic initiative that would push forward the digital transformation of industrial manufacturing.
- They named this initiative Industrie 4.0. It featured an action plan that combined policy initiatives, public–private funding, strategies for technology implementation and the identification of business drivers and barriers.
The difference: For the MLC and its members, Manufacturing 4.0 is made up of transformations in three different arenas: technology, organization and leadership.
- Contrast this with Industry 4.0, which covers only technology topics—specifically nine pillars of technological innovation, which include autonomous robots, big data, cloud computing, IoT, cybersecurity, systems integration, simulation, AR/VR and additive manufacturing.
- “MLC, of course, covers all of these technologies, but, importantly, adds the dimensions of organizational and leadership change as part of its perspective on manufacturing’s digital transformation,” says David R. Brousell, the MLC’s founder, vice president and executive director.
MLC in action: While the MLC does provide member resources that focus on specific technologies and their uses in manufacturing operations, it also covers topics such as how leaders can prepare their workforce for digital transformation, how organizations should be structured to make business decisions based on manufacturing data and how leaders can ensure they set their teams up for digital success.
- Additionally, the annual Manufacturing Leadership Awards recognize not only high-performing digital manufacturing projects but also outstanding individuals who demonstrate both technological understanding and strong personal leadership.
M4.0’s continued evolution: Today, the MLC continues to use Manufacturing 4.0 as the overarching framework for its member companies’ activities.
- Its influence is apparent in the MLC’s annual Critical Issues Agenda, a member-created list of key business drivers and enablers of digital manufacturing.
- The agenda covers technological advances like smart factories and data analytics, alongside the organizational ecosystems that put such advances into operation—from the leaders who direct them to the cultures that make them succeed.
The Future of M4.0: As the MLC gets ready to set its 2023–2024 Critical Issues Agenda, it will continue to take a holistic approach to the technological changes sweeping the industry by recognizing the importance of people in making those transformations happen.
Go deeper: You can learn more about Manufacturing 4.0 by downloading the MLC’s white paper, Manufacturing in 2030: The Next Phase of Digital Evolution; reading a recent report, The Future of Industrial AI in Manufacturing; or attending its Aug. 30 virtual Executive Interview, Shifting from Disruption to Growth.
How Wabash Made Innovation Its Mission

Innovation isn’t just one of many priorities at transportation systems manufacturer Wabash—it’s at the center of everything. Instead of having a traditional R&D function in the product development department, the company has reorganized its hierarchy so that innovation is considered in every major decision, from hiring to investments and more.
“It’s not possible to have innovation siloed in the engineering world; that wouldn’t allow us to achieve the scale of innovation that customers need,” President and CEO Brent Yeagy said.
As the manufacturing supply chain becomes increasingly intricate in a complex world, Wabash is staying ahead of the game. In a recent interview, Yeagy explained how the company does it.
The big picture: This “full reimagining” of the company occurred in response to broad forces reshaping the manufacturing industry, said Yeagy.
- Within the past decade, e-commerce has totally disrupted the logistics model of the previous 30 years, he pointed out.
- Meanwhile, digital technology has enhanced the speed and precision of the industry, which has also increased the complexity of its logistics needs.
- On top of that, the pandemic altered manufacturers’ thinking about lean inventories, lead times and the domestic supply chain infrastructure, sparking a system-wide transformation that isn’t over yet.
- And that’s all before we get to the possibilities of artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles, and new sources of clean energy—all of which could bring profound and unpredictable changes to the industry.
The response: Watching these changes unfold, Yeagy and his team knew they had to take dramatic steps to keep up.
- “We restructured the entire organization away from standalone divisions,” prioritizing collaboration instead, Yeagy said. This involved “aggregating R&D and business development,” which had previously been spread out over 11 different departments.
- This shift also reflected a change in the company’s philosophy. Innovation could no longer be incremental, Yeagy determined, but had to be audacious.
The internal system: Such advances are only possible if the company has a flexible, fast-moving core of innovators who are always looking for the next opportunity, Yeagy told us.
- Instead of creating an innovation strategy that “sits on a shelf” for a year or more, Wabash updates its strategy on a weekly or monthly basis.
- While the company’s R&D and corporate development teams have strict objectives, they can also challenge the strategic direction and introduce fresh ideas—such as new technologies that might give the company an edge.
- This system also requires the right people for the job. Team members must have not only the technical qualifications for the work, but also the capacity to trust, collaborate and be vulnerable when sharing ideas, Yeagy said.
The successes: The company’s new structure has led to industry-leading innovations like Wabash’s subscription model, which allows clients to “subscribe” to a certain level of fleet capacity, instead of managing a fleet of trucks themselves.
- Wabash manages the fleet and maintenance, Yeagy explained, guaranteeing a certain capacity every day to its customers, while offering a range of rental models to suit their needs.
- In another victory for its innovative corporate development team, Wabash found a swift solution when it discovered it didn’t have sufficient distribution capabilities for aftermarket parts. It created a joint venture with a competitor company that had ample warehouse space across the country—going from the idea stage to nationwide operations in a mere six months.
Military influence: Yeagy’s service in the Navy shaped his leadership throughout the company’s transformation, he told us.
- “The military is based on a mission orientation,” he explained. “If everyone understands where we are supposed to go and why, it allows them to be agile and overcome obstacles” in the field, where the unpredictable happens.
- “Officers live to complete the mission by taking care of their people, preparing them mentally, physically, operationally,” and then allowing them to operate on their own. “We have to do that too,” he concluded.
A word of advice: Yeagy advises manufacturing leaders that truly experimental teams require “a safe place to fail and learn how to be comfortable with failure.” He admits that “It’s very hard to take a manufacturing company that doesn’t want to fail, and to teach them,” so leaders must strive to be “immensely” empathetic. It’s clear from speaking to Yeagy that this is his top priority.
China’s Legacy-Chip Investments Trouble U.S., Europe

The U.S. and Europe are working to address “China’s accelerated push into the production of older-generation semiconductors,” Bloomberg (subscription) reports.
What’s going on: Last year, the U.S. imposed restrictions on the export of certain advanced technologies to China. Beijing has reacted by investing heavily in building facilities making older chips that do not face such U.S. restrictions.
- Legacy chips—those produced using 28-nanometer-and-larger equipment—remain critical in the global economy as components of everything from electric vehicles to military devices.
- China is on track to build 26 semiconductor factories through 2026, while the U.S. is forecast to construct 16 facilities “that use 200-millimeter and 300-mm wafers.”
Why it’s a problem: “Senior EU and U.S. officials are concerned about Beijing’s drive to dominate this market for both economic and security reasons, [sources] said. They worry Chinese companies could dump their legacy chips on global markets in the future, driving foreign rivals out of business…”
- If that were to happen, Western firms could become reliant on China for the chips, the sources say, and that could pose a national security risk.
Importance of legacy chips: The global pandemic demonstrated that older-model semiconductors remain important, as chip shortages hit companies’ bottom lines.
- The U.S. and Europe have been trying to expand their own chip production to avoid a repeat. Efforts have included the 2021 CHIPS and Science Act, which set aside $52 billion to bolster domestic semiconductor manufacturing in the U.S.
A problem to solve: “Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo alluded to the problem during a panel discussion last week at the American Enterprise Institute. ‘The amount of money that China is pouring into subsidizing what will be an excess capacity of mature chips and legacy chips—that’s a problem that we need to be thinking about and working with our allies to get ahead of,’ she said.”
Finding Solutions for a Sustainable Manufacturing Future

With increased pressure from customers, regulators and even shareholders, sustainable business practices are no longer optional for manufacturers. From reduced energy and materials consumption to lower emissions and ethical sourcing, manufacturers are expected to meet ambitious new goals. Luckily, the Manufacturing Leadership Council has established a new member working group devoted to helping manufacturers reach these objectives.
Support set-up: With five virtual meetings each year, the M4.0 Sustainability and Net Zero Decision Compass Group will explore key issues, best practices and challenges related to creating sustainable, compliant and environmentally friendly operating strategies.
- At the first meeting, “Next Steps in Manufacturing 4.0 Sustainability,” on March 10, attendees heard from 3M Senior Vice President of Environmental Strategies and Fluorochemical Stewardship Dr. Rebecca Teeters and Lexmark International Chief Sustainability Officer John Gagel. Both speakers are also MLC board members.
Why the new group: The MLC decided to create the group after a survey of their more than 3,300 members revealed sustainability was a top member business concern.
- “We decided that given the intensity of interest in sustainability and related subjects, such as net zero and the circular economy, this was an opportunity to dedicate a whole new group to the topic,” said MLC Co-Founder, Executive Director and Vice President David Brousell.
Good for business, too: While manufacturers have been discussing and working toward sustainability for decades, recent growing concerns about climate change and other environmental issues are making the matter increasingly urgent.
- Manufacturers that take on sustainable business practices are seeing competitive advantages ranging from cost savings to higher product quality to increased shareholder and employee satisfaction.
Lessons from manufacturing peers: The new Decision Compass group will share sustainability strategies, the real-world achievements of manufacturing companies, knowledge about the use and application of advanced technologies and timelines for implementation.
- Participants will also be able to see how they stack up against other manufacturing companies.
Get involved: The MLC offers resources to help manufacturers improve their operations and learn about digital manufacturing. To learn more about the sustainability group or find out about MLC membership, email [email protected].
STEP Ahead Awards Honor Women in Manufacturing

The Manufacturing Institute’s 10th annual STEP Ahead Awards took place in Washington, D.C., last week, honoring some of the most impressive and inspiring women in the manufacturing industry today. The Awards are part of the STEP Ahead program, which is designed to help advance women’s achievements in the fields of science, technology, engineering and production.
- The event highlighted the 2022 STEP Ahead Honorees (100 women who are leaders in manufacturing) and the 2022 STEP Ahead Emerging Leaders (30 women under 30 years old who have already had a significant impact on the industry).
The awards ceremony took place on Thursday night, with hundreds of guests in attendance at the National Building Museum and hundreds more viewing the ceremony online. The program featured:
- 2022 STEP Chair and former 3M Senior Vice President Denise Rutherford;
- 2022 STEP Vice Chair and Cornerstone Building Brands President and CEO Rose Lee;
- MI President Carolyn Lee;
- MI Vice President of Strategic Engagement and Inclusion AJ Jorgenson; and
- NAM President and CEO and MI Board Chair Jay Timmons.
Sponsors included an all-star roster of manufacturers, including Arconic Foundation, BASF Corporation, Cornerstone Building Brands, PTC, Trane Technologies, ABB, Molson Coors, Novelis, Rockwell Automation, SABIC, Sherwin-Williams and Toyota.
What they said: Carolyn Lee lauded the Honorees and spoke about the importance of closing the skills gap by bringing more women into the manufacturing industry.
- “My hope is that 10 years down the line, when we meet here for the 20th anniversary of these awards, the young women we will honor won’t have even heard of the glass ceiling, because it’ll be ancient history,” said Lee.
- “And that will be thanks to the support system, the mentorship and the sterling examples set by the women in this room and the support from our allies.”
Rutherford spoke about leaders’ opportunities to work together to make important progress.
- “Throughout my career, I’ve learned that being a great leader, as an individual or as a company, means that we don’t go it alone,” said Rutherford. “True change only happens when we work together as trusted allies, advocates and sponsors.”
Rose Lee laid out the qualities that all the Honorees showed and highlighted their shared successes.
- “The STEP Ahead Awards recognize women in science, technology, engineering and production who exemplify leadership within their companies and within their communities,” said Lee. “Tonight is their night to celebrate their accomplishments.”
Timmons praised the STEP Honorees and called on allies to continue supporting women in the manufacturing industry.
- “Your achievements, your success and your dedication are showing women what’s possible in manufacturing,” he said. “If you can see it, you know you can be it.”
35×30: Carolyn Lee and Jorgenson spoke about the 35×30 initiative—a program designed to close the skills and talent gap in manufacturing by adding half a million women workers to the industry, increasing women’s representation in manufacturing from 29% today to 35% by 2030.
- The campaign will train more than 1,000 women mentors, build new tools and resources and work with manufacturing leaders to deploy proven strategies to attract and retain female talent.
- It will also support young women throughout their education by offering best-in-class leadership development programming and creating a STEP alumnae-funded scholarship.
- “Tonight, we are done with waiting for other leaders to ‘change things,’ to make society better, more equitable,” said Jorgenson. “We are the leaders. So, tonight, we ask you to join us, to lead.”
New commitments: To help this new initiative along its way, Arconic Foundation President Ryan Kish and Ketchie CEO Courtney Silver stood up during the ceremony to pledge new financial commitments to the program.
The last word: The gala featured a stellar musical performance by award-winning singer–songwriter Rachel Platten, which left not a dry eye in the house. Inspired by the women of STEP, she surprised the audience by singing a new song she’d written for her daughters. It captures what the women leaders of today want to tell the girls who will someday be their heirs:
Girls, you were born to run. To reach the stars and chase the sun.
Girls, you’re wild and free. The wind is at your back, the world is at your feet.
CHIPS Office Has Unique Job to Do

A new Commerce Department office tasked with dispensing tens of billions of federal funding for domestic semiconductor manufacturing faces a challenging job, according to Roll Call.
What’s going on: “The experts at the CHIPS program office are charged with enticing the world’s largest chipmakers to the U.S. to fashion cutting-edge semiconductors used in weapons and supercomputers, as well as in more ordinary devices like thermostats. The goal is to break the dependence that many American manufacturers of missiles, spy satellites, telecom gear and medical devices have on suppliers primarily based in Taiwan and South Korea.”
- Congress allocated $52 billion for the effort last year.
Why it’s important: “Deploying taxpayer funds and the federal government’s power puts the department and the CHIPS office in a unique position of executing a novel industrial policy: one focused on both national security as well as economic well-being, and one that is expected to back manufacturing plants as well [as] research and development efforts.”
- In recent decades, the most successful U.S. industrial policy interventions have been similar to this one: funding for “high-risk, high-reward” R&D, according to a Peterson Institute study cited by Roll Call.
Making it count: Sens. Mark Warner (D-VA) and John Cornyn (R-TX) are adamant that the money must be doled out judiciously.
- “This is not an economic proposition,” Sen. Cornyn said. “It’s obviously important from an economic standpoint, but national security is the main reason why Sen. Warner and I undertook the legislation.”
Keen interest: The new office has received more than 400 statements of interest from semiconductor manufacturers. Preliminary applications will be accepted starting in September.
- Top chipmakers, including Intel and others, “have indicated they may invest as much as $400 billion in the U.S. provided they get some support from the government.”
- Six expert teams will review the applications and decide on the amounts each firm will receive. National security experts will weigh applications based on companies’ security measures and supply chain resiliency capabilities.
The NAM says: “Bolstering domestic chip manufacturing is a security and economic imperative for the U.S.,” NAM Director of Domestic Policy Julia Bogue said.
- “That’s why the NAM supported passage of the CHIPS and Science Act and continues to advocate for actions that will see the U.S. manufacturing more semiconductors.”
Wisconsin Manufacturers & Commerce Honored with 2023 Leadership Award from Conference of State Manufacturers Associations
Bluffton, S.C. – Today, the Wisconsin Manufacturers & Commerce was honored with the 2023 Leadership Award from the Conference of State Manufacturers Associations, whose members also serve as the National Association of Manufacturers’ official state partners and drive manufacturers’ priorities on state issues, mobilize local communities and help move federal policy from the ground up in all 50 states and Puerto Rico. WMC was recognized for their work to attract and maintain the manufacturing workforce.
“We congratulate Kurt Bauer and the entire team at WMC for their incredible work this year to not only educate the next generation of manufacturing workers in Wisconsin, but also engage the business community at large to help spur investment in the state,” said Utah Manufacturers Association President and CEO, NAM board member and COSMA Chair Todd Bingham. “Their work shows the impact that we can all have to help make the United States the top destination in the world for manufacturing investment.”
The Leadership Award recognizes the achievement of a state manufacturing association that has developed impactful initiatives to support manufacturers and strengthen manufacturing in their state. Some of the initiatives that set WMC apart were their Coolest Thing Made in Wisconsin and Business World, which teach young people about entrepreneurship and free enterprise and promote manufacturing job opportunities in the state. Additionally, as part of WMC’s official mission to make Wisconsin the best place for business, the Future Wisconsin Project brings together diverse interest groups to identify and address the state’s long-term economic challenges and opportunities, including solutions to workforce challenges.
“The work of WMC to inspire the workforce of the future is a prime example of what’s needed to address the critical challenges that our sector faces today,” said NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons. “Under Kurt Bauer’s leadership, the WMC is advancing the solutions needed to make manufacturers more competitive and ensure manufacturing remains a key driver of Wisconsin’s economy.
-NAM-
The National Association of Manufacturers is the largest manufacturing association in the United States, representing small and large manufacturers in every industrial sector and in all 50 states. Manufacturing employs nearly 13 million men and women, contributes $2.91 trillion to the U.S. economy annually and accounts for 55% of private-sector research and development. The NAM is the powerful voice of the manufacturing community and the leading advocate for a policy agenda that helps manufacturers compete in the global economy and create jobs across the United States. For more information about the NAM or to follow us on Twitter and Facebook, please visit www.nam.org.
NAM Advances Manufacturing Priorities at USMCA Meeting in Mexico
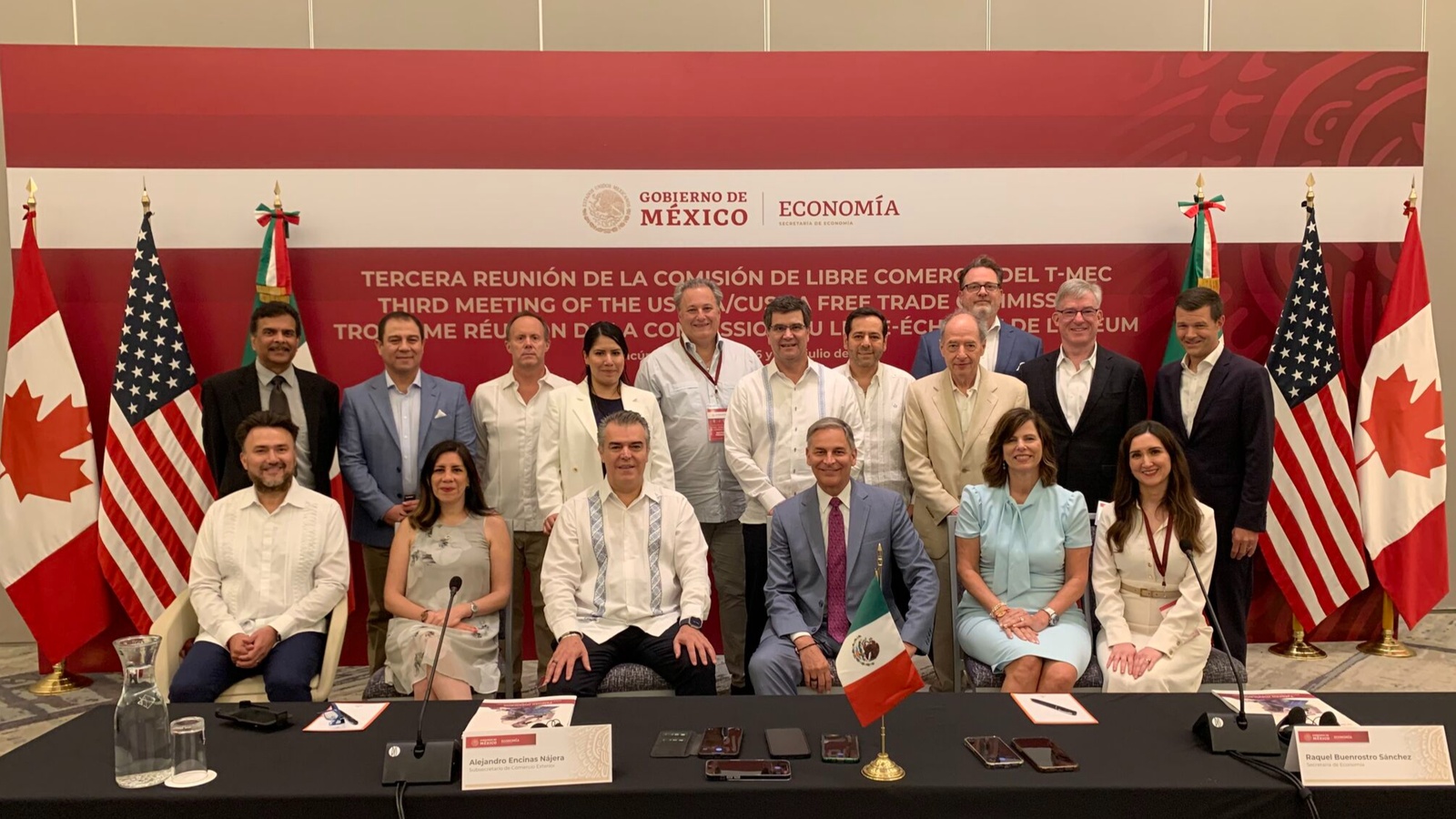

The NAM met with North American trade ministers last week in Cancun, Mexico, where it urged them to take up key trade priorities for manufacturers.
What happened: The NAM led a delegation from the American business community, which participated in a roundtable discussion ahead of the third United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement “Free Trade Commission” on July 7 in Cancun.
- Attendees at the roundtable event included NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons, U.S. Trade Representative Katherine Tai, Canadian Minister of Small Business, Export Promotion and International Trade Mary Ng, Mexican Secretary of the Economy Raquel Buenrostro and business executives from the three countries, including Rockwell Automation Chairman and CEO Blake Moret.
Shared values: The NAM underscored the importance of an investment climate underpinned by core democratic principles, such as transparency and the rule of law.
- “We believe in democracy,” Timmons said. “However imperfect, this system fosters free enterprise, competitiveness, individual liberty and equal opportunity. These values make manufacturing strong in our countries.”
- He added that each year North American manufacturers contribute $3 trillion to the U.S., Canadian and Mexican economies.

What must be done: Though the USMCA already creates advantages for North American manufacturers, the agreement’s full potential can only be realized if the three countries work together to address certain key challenges, Timmons told the attendees. Some of the main hurdles include:
- Mexico’s power-generation policies, which have long favored Mexican state-owned energy companies and led to higher bills for manufacturers that must use existing energy-supply contracts;
- Permitting delays for U.S. projects in Mexico that undercut American firms and reduce energy supply to North American manufacturers and consumers;
- Mexico’s expanded food-labeling requirements and bans on the sale of some U.S. foods and nonalcoholic beverages to minors, which unjustly restrict U.S. exports;
- High spectrum fees in Mexico that deter telecommunications competition, as well as the country’s weak patent enforcement, delayed approvals of pharmaceuticals and bans on certain chemicals and genetically modified corn; and
- Delays in the reform of Canada’s patent system, ongoing restrictions in Canada’s dairy market, a Canadian government proposal to brand “plastic manufactured items” as “toxic substances” and a change to Quebec packaging and labeling requirements that will upend decades of intellectual property law and could limit access to the Quebec market.
The last word: “Ensuring North American economic integration and regional competitiveness will require a multipronged effort that focuses on robust implementation of the USMCA, ensuring a competitive North American energy market and providing support for the manufacturing workforce across the region, among other key elements,” said NAM Vice President of International Economic Affairs Ken Monahan, who joined Timmons in Cancun.
- “The NAM has positioned itself as a leading U.S. business organization on North American trade and economic matters, and we look forward to continuing to engage with our member companies on these issues going forward.”
Semiconductor Makers Look to “Chiplets”

The explosive growth of artificial intelligence is leading semiconductor makers to move quickly to create “designs that stack chips together like high-tech Lego pieces,” according to The Wall Street Journal (subscription).
What’s going on: “‘Chiplets’ can be an easier way to design more-powerful chips, according to industry executives who call the technology one of the most significant advances since the dawn of the integrated circuit more than 60 years ago.”
- The technology has the potential to deliver more powerful, cost-effective semiconductors, sources told the Journal.
- Last year, some of the world’s largest technology companies, including Qualcomm and Intel—which recently announced products containing chiplets—formed a coalition to craft chiplet-designing standards.
How it works: “A typical consumer device such as a smartphone contains many types of chip[s] for functions including data processing, graphics processing, memory, telecommunications and power control.”
- “The chips are delicately tethered to minuscule wires and ensconced in a protective plastic casing, forming a package that can be fixed to a circuit board.”
- “With the new chiplet packaging, engineers have found ways to bolt together pre-existing chips, the equivalent of using a few Lego pieces to build a toy car.”
The caveats: Chiplet manufacturing is not cheap, however, and the technology requires its own performance-verification process.
- What’s more, chiplets “aren’t suited to every function,” and lend themselves better to high-end desktop computers than mass-marketed cell phones.
China’s role: It is estimated that China controls 38% of the semiconductor assembly, testing and packaging market, a fact that “poses two potential risks for the U.S. While many American companies have been working with factories in China to handle these specialist chip-making roles, the supply chains could be tangled by a geopolitical crisis or another pandemic.”
- “In addition, the U.S. has imposed export controls on advanced semiconductor technology and could seek to expand controls in the future.”
NAM Advances Manufacturing Priorities at USMCA Meeting in Mexico

The NAM met with North American trade ministers last week in Cancun, Mexico, where it urged them to take up key trade priorities for manufacturers.
What happened: The NAM led a delegation from the American business community, which participated in a roundtable discussion ahead of the third United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement “Free Trade Commission” on July 7 in Cancun.
- Attendees at the roundtable event included NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons, U.S. Trade Representative Katherine Tai, Canadian Minister of Small Business, Export Promotion and International Trade Mary Ng, Mexican Secretary of the Economy Raquel Buenrostro and business executives from the three countries, including Rockwell Automation Chairman and CEO Blake Moret.
Shared values: The NAM underscored the importance of an investment climate underpinned by core democratic principles, such as transparency and the rule of law.
- “We believe in democracy,” Timmons said. “However imperfect, this system fosters free enterprise, competitiveness, individual liberty and equal opportunity. These values make manufacturing strong in our countries.”
- He added that each year North American manufacturers contribute $3 trillion to the U.S., Canadian and Mexican economies.
What must be done: Though the USMCA already creates advantages for North American manufacturers, the agreement’s full potential can only be realized if the three countries work together to address certain key challenges, Timmons told the attendees. Some of the main hurdles include:
- Mexico’s power-generation policies, which have long favored Mexican state-owned energy companies and led to higher bills for manufacturers that must use existing energy-supply contracts;
- Permitting delays for U.S. projects in Mexico that undercut American firms and reduce energy supply to North American manufacturers and consumers;
- Mexico’s expanded food-labeling requirements and bans on the sale of some U.S. foods and nonalcoholic beverages to minors, which unjustly restrict U.S. exports;
Read the full story here.