State of Manufacturing: Strong, But Not Guaranteed
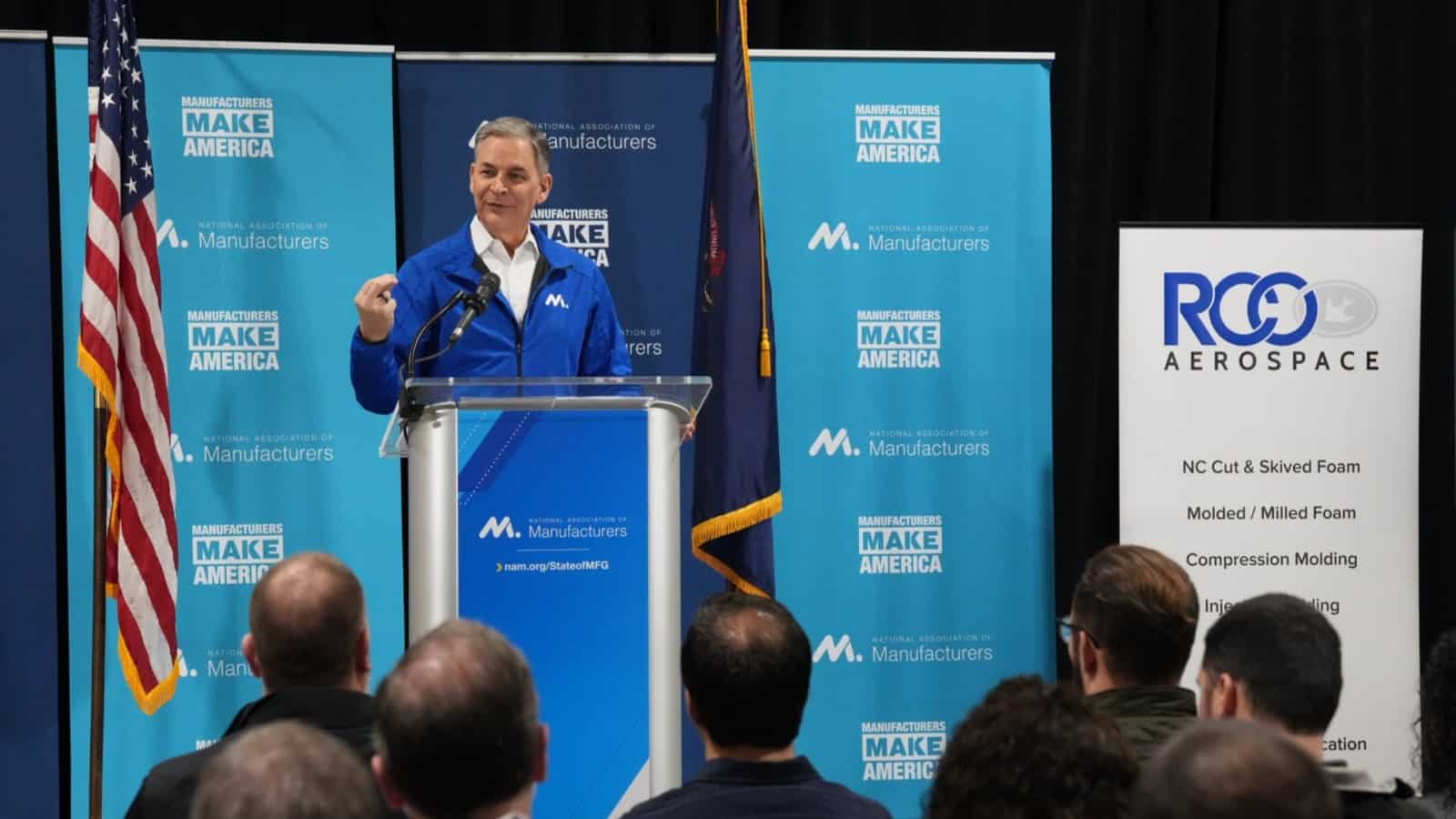

What’s the state of manufacturing in the U.S.? Strong and resilient—but under threat.
That was the message delivered by NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons and other speakers at the NAM’s 2024 State of Manufacturing Address at RCO Engineering in Roseville, Michigan, on Thursday.
- Attending the address were nearly 100 RCO Engineering team members—some of whom are second- or even third-generation manufacturing workers—as well as local education leaders, including Macomb Community College President James O. Sawyer IV and Macomb Intermediate School District Superintendent Michael R. DeVault.
- The address was the keystone event of this week’s launch of the 2024 Competing to Win Tour, an opportunity to visit local manufacturers and report on where the industry stands at the start of 2024.
A place of strength: “The state of the manufacturing industry depends on the people in it,” Timmons said in remarks covered by POLITICO Influence (subscription). “And we are now 13 million strong—the largest in more than 15 years. If we can continue on this trajectory, this resurgence, imagine what the state of manufacturing might look like in 2030.”
- Johnson & Johnson Executive Vice President and Chief Technical Operations & Risk Officer and NAM Board Chair Kathy Wengel echoed that sentiment in her opening remarks. “Manufacturers are improving the quality of life for everyone. … Together, we can lead the way.”
- And Michigan Manufacturers Association President and CEO John Walsh told the audience at RCO Engineering, “You are making parts here that are going everywhere. It’s a phenomenal story for us in Michigan. It not only helps you as employees here, but it helps your families, it helps your communities. It builds our state. It builds our nation.”
- “Manufacturing … is an industry that is vital to our economic competitiveness,” said Macomb County Executive Mark Hackel. “In Macomb County, we’re not just witnessing the growth of manufacturing; we’re actively contributing to it. What we are doing here is creating an environment where innovation thrives and where manufacturers can grow as well as compete.”
- RCO Engineering General Manager Jeff Simek agreed. “The manufacturing brand is coming back, and it’s coming back alive—and you guys are a big, huge piece of that,” he said to loud applause.
Fork in the road: But continued manufacturing strength isn’t guaranteed, Timmons said. Rather, it’s in large part contingent on sound policy decisions by U.S. leaders.
- “We will head in the wrong direction if Congress lets taxes go up on small businesses when rates expire next year,” Timmons said. “Or if they hit you with even more regulations—regulations even harsher than ones they have in Europe. Or if they fail to solve the immigration crisis because they put politics over good policy. Or choose trade barriers rather than trade agreements, or … abandon our allies overseas and put our national security at risk.”
- The recent regulatory onslaught by federal agencies—which Timmons discussed with Fox Business earlier this week—must stop and be replaced with sensible rulemaking done in cooperation with manufacturers, he said.
- He cited the Environmental Protection Agency’s recently finalized, overly stringent standard for particulate matter and the Biden administration’s decision to freeze liquefied natural gas export permits. This “forc[es] our allies, like Europe and Japan, to buy dirtier energy from countries we can’t trust, potentially enriching the likes of Russia … undercut[ting] our most basic national security objectives,” Timmons said.
No new taxes: The NAM’s message to Congress on taxes is simple: “No new taxes on manufacturers in America,” Timmons said.
- “And while we’re at it, Congress should bring back some of the tax policies that made it easier for manufacturers to invest in the future.”
On immigration: The U.S. needs a common-sense solution to immigration, and it needs it now, Timmons said.
- While manufacturers may not like every piece of the bipartisan border deal that was recently killed in the Senate, “here was my test: Does it make us more secure than we are today? Yes. Does it make our workforce stronger than it is today? Yes. And does it help our allies overseas? Yes,” said Timmons.
Come what may: No matter what the November elections bring, manufacturers will continue to do the jobs so many people depend on them to do, Timmons concluded.
- “Our commitment is to work with anyone, and I truly mean anyone, who will put policy—policy that supports people—ahead of politics, personality or process. We will stand with you if you stand with us in advancing the values that have made America exceptional and keep manufacturing strong.”
Trend of the Week: Data in Action

Everyone knows that data is an indispensable resource, but putting it to use is a whole different challenge from collecting it in the first place. Here’s what you need to know about today’s manufacturing trend, the industry’s increasing reliance on data-driven insights.
What manufacturers should do: According to NAM experts, manufacturers seeking to make the most of their data should focus on five key steps:
- Understand how to gather data to enable meaningful analytics.
- Improve data governance for quality and security.
- Determine what data are important to your business and operations.
- Learn how to assign value and view the data through the appropriate lens.
- Know how to use data to make business decisions.
Expert opinion: According to John Petrusick, managing director of NTT’s manufacturing data and analytics practice, companies should consider working backward to some extent, and start by thinking about which business processes the data will influence—and how.
- “Most of us have grown up in a world where we think of data as a flow from source to consumer, or left to right,” he noted. “In such thinking, we have generated analytics and insights historically by first thinking about ‘what data do I have?’ But what if we thought about generating analytics and insights by thinking ‘right to left’?”
Resources for you: Looking for more resources on data management? Start with these NAM offerings:
- This Master Class Series from the Manufacturing Leadership Council (the NAM’s digital transformation division) will guide you through case studies and best practices regarding data analysis.
- CONNEX Marketplace uses data visualization tools to help you make connections to suppliers and buyers, offering exceptional insight into your supply chain.
- The NAM’s Power of Small newsletter keeps small and medium-sized manufacturers up to date on advocacy, policy, digital trends and much more. Check it out.
Read the full 2024 trends report here.
Primary Goals: NAM Hits the Road in 2024

As candidates look to claim the support of manufacturers in 2024, the NAM launched its year-long 2024 Competing to Win Tour in South Carolina, days ahead of the South Carolina GOP primary.
- The tour spotlights the issues critical to winning not just manufacturers’ votes but also more manufacturing in the U.S.
Why it’s important: “We came to South Carolina to showcase the people and stories behind our industry and to translate their perspectives into action that will make our industry and country stronger,” said Johnson & Johnson Executive Vice President and Chief Technical Operations & Risk Officer and NAM Board Chair Kathy Wengel, who joined NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons, South Carolina Chamber of Commerce President and CEO Bob Morgan and South Carolina Manufacturers Alliance President and CEO Sara Hazzard on the first day of the tour.
- “Building these strong relationships beyond Washington, D.C., in the cities and states driving our sector deepens our understanding of regional challenges and reinforces the NAM as the leading voice representing all manufacturers, large and small,” Wengel added.
The launch: The tour began at Milliken & Company’s headquarters in Spartanburg on Wednesday, a poignant reminder of the importance of just one global technology-based manufacturer to lives, innovation and progress.

- The company’s 3,200 associates in the Palmetto State, as well as its broader U.S. and global team, make everything from safety gear and wound dressings and bandages to eco-conscious materials and technological innovations, such as digital printing, flooring, sustainable coating additives and more.
- “The average person touches about 30 to 50 [Milliken products] a day,” said Milliken President and CEO Halsey Cook.
- “Milliken embodies what we believe: manufacturing makes a positive difference. Their commitment to sustainability, ethics (named a World’s Most Ethical Company 17 years running) and a people-first workplace create a ripple effect,” said Timmons. “It’s why we need everyone supporting the success of manufacturers in South Carolina and the United States—to empower companies just like Milliken and help us grow more of them right here in America,” Morgan emphasized.
- “Milliken is a remarkable brand ambassador for the entire manufacturing industry in the United States,” summed up NAM Managing Vice President of Brand Strategy Chrys Kefalas. “As Michael Brown, Milliken’s executive vice president of operations, conveyed to us, the company is showing that digital transformation and artificial intelligence can be a force for good, helping its people leverage data analytics, for example, accelerating innovation and making modern manufacturing even more exciting for the next generation to be a part of.”
A boom story: Springs Creative Products Group CEO Derick Close, who heads several small enterprises in South Carolina, brought the NAM tour to Fort Lawn, South Carolina, where state-private partnerships and sound competitiveness policies have led to a boom in manufacturing investment and jobs.
- According to Close, recent investments in the community exceed $2.5 billion and stand to add 1,500 new jobs.
- Close, who is an economic development champion for South Carolina, took time to brief the group on how the area is ground zero as well in the story of the revival—and revolution—happening for the U.S. textile manufacturing sector, showing that U.S.-based textile manufacturers can compete against the rest of the world at quality, speed and price, so long as misguided policies don’t impede current advances. Springs Creative’s digital printing facility, which the NAM toured, is just one example. Springs Creative produces fabrics for such companies as Disney, Tempur-Pedic and Walmart.
- An added highlight of Close’s showcase was a tour of the new 1.5-million-square-foot, $423 million E. & J. Gallo wine and spirits production and distribution center—a testament to U.S. ingenuity and the more than 275 jobs it’s already created (with more on the way) to produce the best-selling spirit in the U.S.

The message: The discussions at Milliken and Springs Creative focused on the need for policies that support manufacturing’s growth, from R&D incentives and competitive taxes to sensible regulations, resilient supply chains and permitting reform, to workforce development, including immigration reform, and energy policy.
The platforms: As newsrooms dwindle, the NAM is stepping into the breach, using its platforms, like NAM.org, social media and its email newsletters, including Input, to amplify manufacturing’s narrative. It’s a bid to ensure that as policymakers and candidates court manufacturers, they’re armed with real stories and concrete policy needs from the ground.
Looking ahead: The tour will continue across the United States, gathering insights and stories to bolster the NAM’s advocacy efforts. Next up: the Competing to Win Tour brings the NAM State of Manufacturing Address to Roseville, Michigan, as well as to Sanders Chocolate and Triumph Gear Systems in Macomb County on Thursday.
GlobalFoundries to Get $1.5 Billion in CHIPS Funding

Semiconductor maker GlobalFoundries Inc. will be the first recipient of funding under the NAM-supported 2022 CHIPS and Science Act, CNBC reports.
What’s going on: “The U.S. government is awarding $1.5 billion to GlobalFoundries to subsidize semiconductor production, the first major award from a $39 billion fund approved by Congress in 2022 to bolster domestic chip production.”
- The Malta, New York–based GlobalFoundries—the largest U.S. manufacturer of customized semiconductors and the world’s third-biggest chipmaker—plans to use the funds to build a new chip-production facility in its hometown and expand existing facilities there and in Burlington, Vermont.
- The Malta facility will manufacture high-value semiconductors not currently produced in the U.S., Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo said.
- In addition to the grant, the federal government is also offering GlobalFoundries $1.6 billion in loans.
Why it’s important: “The chips that GlobalFoundries will make in these new facilities are essential chips to our national security,” Raimondo said on Sunday, adding that the “agency is in active talks with numerous applicants and expects to make several announcements by the end of March.”
- In January, Commerce announced it was awarding defense contractor BAE Systems $35 million under the CHIPS Act.
Our role: The NAM—which helped secure several manufacturing priorities in the final CHIPS Act legislation—welcomed the news.
- “Congratulations to [GlobalFoundries]!” the NAM wrote in a social post Monday. “The NAM-championed CHIPS and Science Act is strengthening manufacturing in the U.S. We will continue to work with Congress and the White House to enact permitting reforms that will help speed the construction of these vital projects.”
Trend of the Week: Sustainability Under Scrutiny

Manufacturers have long prioritized sustainability in their operations, but 2024 will bring new attention to the industry’s efforts. As we continue to explore the major manufacturing trends that will shape the industry this year, here’s what you need to know about this key development.
What manufacturers should do: Manufacturers looking to create strong sustainability plans to meet the expectations of regulators, boards and consumers should start by taking these steps, according to the NAM’s experts.
- Craft an overall organizational sustainability plan with metrics and reporting.
- Make changes and upgrades to support energy and resource efficiency, as well as reduce waste and emissions.
- Focus on sustainable products and packaging in addition to sustainable processes.
- Improve product reclamation or recycling in the circular economy.
Expert opinion: According to UL Solutions, company boards have a particularly key role to play in developing sustainability plans.
- “Boards of directors are bound by their fiduciary responsibilities to shareholders, but savvy directors also recognize that environmental and other ESG-linked risks and opportunities are vital to the long-term health of their organizations,” UL notes.
Resources for you: Check out these NAM resources to learn more about sustainability and compliance:
- NAM Energy will connect you with an adviser to create an energy management strategy that will help you cut costs and reduce your environmental impact.
- This podcast from Milliken & Company’s director of research, compliance and sustainability is an excellent case study for manufacturers seeking to remove or remediate PFAS chemicals.
- Dig into the NAM’s extensive collection of policy explainers, on everything from the Environmental Protection Agency’s regulation of particulates to the Securities and Exchange Commission’s regulation of climate disclosures.
Read the full 2024 trends report here.
What’s Ahead for Manufacturing in 2024?

Getting a solid forecast of the year’s key issues in manufacturing can help your business prepare for anything. A panel of experts recently shared their 2024 outlook in the webinar “What’s Ahead for Manufacturing in 2024?” hosted by the Manufacturing Leadership Council, the NAM’s digital transformation arm.
They offered insights on the 2024 manufacturing economy, legislative climate, digital trends, resilience strategies and more.
Economic outlook: NAM Chief Economist Chad Moutray provided a manufacturing economic update.
Key takeaways:
- The NAM Q4 2023 Manufacturers’ Outlook Survey revealed that more than 66% of member companies have a positive economic outlook for 2024, yet opinions are mixed on whether there will be a recession.
- The top economic challenge this year will be the workforce, with the labor market cooling substantially but remaining tight, Moutray said.
- Private manufacturing construction spending is at an all-time high of $210 billion thanks to the production of semiconductors, electric vehicles and batteries, and general reshoring.
- Risks this year include geopolitical turmoil, slow global economic growth, cost pressures, talk of a recession and labor issues, among others.
Policy perspective: NAM Vice President of Domestic Policy Charles Crain gave an overview of the current climate in Washington, D.C., and the NAM’s legislative priorities.
Key takeaways:
- The NAM will continue its focus on tax policy following House passage of an NAM-supported bipartisan tax package that would reinstate three manufacturing-critical tax provisions.
- Manufacturing is facing a regulatory onslaught, with the average manufacturer paying $29,000 per employee per year due to unbalanced, burdensome regulations, according to a recent NAM-commissioned study.
- Artificial intelligence is a hot topic on Capitol Hill, with 60 AI-related bills introduced in Congress last year. The NAM is working to help policymakers understand the benefits of AI, including safety, worker training, product design and development, and efficiency.
Manufacturing 4.0 Trends: MLC Senior Content Director Penelope Brown offered a look at digital manufacturing trends on the horizon.
Key takeaways:
- Manufacturers can expect to see a broader adoption of existing AI applications, including predictive/preventative maintenance, improved processes and enhanced productivity.
- According to the MLC’s recent Smart Factories and Digital Production survey, 65% of manufacturers anticipate their level of M4.0 investment this year will stay the same as last year.
- Other trends to watch include the rise of global partnerships such as Catena-X and CESMII, digitized supply chains and reshoring.
Resilience perspective: Cooley Group President and CEO (and MLC Board of Governors Chair) Dan Dwight shared his approach to resilience in 2024 and the years to come.
Key takeaways:
- Business leaders should prioritize agility and adaptability, even if it means admitting to suboptimal results that require redirection.
- Resilience doesn’t mean perfection; it means learning from failures.
- AI and machine learning contribute to resilience by building out end-to-end visibility across an organization—from vendors to manufacturing operations to customers.
For additional details from these experts, watch “What’s Ahead for Manufacturing in 2024?”
March-In Proposal Undermines IP Rights, Hurts Manufacturers

The Biden administration’s proposal to invoke so-called “march-in” authority to seize the rights to patents developed in any part with federal funding would undermine the American innovation economy, the NAM told the federal government Tuesday.
What’s going on: A proposal put forth in December by the Biden administration would allow the government to seize private-sector patents for products it considers too costly.
Why it’s important: “Undermining manufacturers’ [intellectual property] rights would have sweeping ramifications for innovation in the United States and America’s world-leading innovation economy,” the NAM told the Biden administration.
- “In particular, start-ups and small businesses would bear the brunt of the drastic changes proposed by the administration, as … government march-in would disincentivize early-stage entrepreneurship and dissuade much-needed capital formation from outside investors.”
The background: The Bayh-Dole Act, passed in 1980, allows recipients of federal research dollars to license groundbreaking technologies to private-sector companies to commercialize them.
- “Prior to the act’s passage, the government held approximately 28,000 patents—yet fewer than 4% of those patents were licensed to the private sector. This is because private-sector participants viewed these patents as ‘contaminated by government funding,’” according to the NAM.
- Bayh-Dole includes a narrow “march-in” provision that allows the government to step in to ensure consumer access to certain products during times of crisis—but march-in “has never previously been used during the 44 years since the law’s enactment,” the NAM said.
- Allowing march-in based on the price of a product or technology “would hinder industry collaborations with research universities and laboratories across the country, stymieing manufacturers’ efforts to develop the products and technologies of the future and bring them to the public.”
What we’re doing: Last month, the NAM launched a seven-figure ad campaign opposing the proposal.
- The administration should “provide certainty to manufacturers and other stakeholders in the innovation economy by affirmatively and unequivocally withdrawing the proposal—and making clear that the administration will not implement any of its recommendations,” the NAM said.
The last word: “Undermining America’s world-leading patent system is a recipe for reduced innovation and significant economic damage, with a disproportionate impact on small manufacturers,” said NAM Vice President of Domestic Policy Charles Crain.
- “The administration’s march-in proposal would raise the spectre of government price controls on a wide range of technologies—fundamentally reshaping how life-changing innovation is developed, financed and commercialized in the United States. The administration must affirmatively and unequivocally withdraw this radical and flawed proposal.”
ICYMI: NAM Opposes Biden Administration’s Proposal to Undermine Manufacturers’ IP Rights
Washington, D.C. – Following the National Association of Manufacturers’ submission of comments opposing the Biden administration’s proposal that would allow the government to march in and seize the rights to groundbreaking innovations developed by manufacturers, NAM Vice President of Domestic Policy Charles Crain released the following statement:
“Undermining America’s world-leading patent system is a recipe for reduced innovation and significant economic damage, with a disproportionate impact on small manufacturers. The administration’s march-in proposal would raise the spectre of government price controls on a wide range of technologies—fundamentally reshaping how life-changing innovation is developed, financed and commercialized in the United States. The administration must affirmatively and unequivocally withdraw this radical and flawed proposal.”
The NAM’s comments on the proposal are available here. Key excerpts from the comments are below:
- The proposal contemplates an expansion of the Bayh-Dole Act’s march-in provision, which has never previously been used during the 44 years since the law’s enactment. This unlawful expansion of a 44-year-old statutory provision would prompt the government to exercise march-in rights to force patent licenses to private-sector inventions that are derived at least in part from federal funding. This price control measure would impact innovative companies of all kinds across the manufacturing sector.
- Undermining manufacturers’ IP rights would have sweeping ramifications for innovation in the United States and America’s world-leading innovation economy. In particular, start-ups and small businesses would bear the brunt of the drastic changes proposed by the administration, as the spectre of government march-in would disincentivize early-stage entrepreneurship and dissuade much-needed capital formation from outside investors.
- If the administration moves forward with the proposal, the unprecedented expansion and use of the Bayh-Dole Act’s march-in provision would impede R&D, investment and the commercialization of innovative technologies. It would cause significant market uncertainty as to current and future patent licenses that are derived in any part from federal funds—directly contradicting the intent and purpose of Bayh-Dole. And it would hinder industry collaborations with research universities and laboratories across the country, stymieing manufacturers’ efforts to develop the products and technologies of the future and bring them to the public.
- Courts have found that an agency violates the major questions doctrine on matters of significant economic importance when the agency cannot “point to clear congressional authorization for the power it claims.” The government’s ability to seize private-sector IP is undoubtedly a topic of vast economic and political significance; as discussed, America’s robust patent system lies at the heart of the innovation economy in the United States—and the proposal would threaten the financing of that innovation ecosystem and the economic viability of many of its key participants (including start-ups, entrepreneurs, small and medium-sized businesses, universities and more). The effects of the proposal would be felt in every state and every congressional district. Yet, the proposal cannot point to “clear congressional authorization” for including a price consideration in the government’s march-in analysis because it does not exist; as explained above, price is wholly absent from the Bayh-Dole Act’s text. More broadly, the act was enacted to support public–private partnerships and bolster the innovation economy in the United States—yet, the proposal would undermine and endanger American innovation. It is unlikely that Congress, in passing the Bayh-Dole Act, “could reasonably be understood to have granted” the administration the power to vitiate the primary goal of the act itself.
- The NAM respectfully encourages the administration to provide certainty to manufacturers and other stakeholders in the innovation economy by affirmatively and unequivocally withdrawing the proposal and making clear that the administration will not implement any of its recommendations. Abandoning and disclaiming the proposal’s attempts to impose price controls and undermine the Bayh-Dole Act will ensure that manufacturers in the United States can continue to lead the world in R&D and innovation—and continue to create and support well-paying jobs vital to the success of the U.S. economy.
-NAM-
The National Association of Manufacturers is the largest manufacturing association in the United States, representing small and large manufacturers in every industrial sector and in all 50 states. Manufacturing employs nearly 13 million men and women, contributes $2.85 trillion to the U.S. economy annually and accounts for 53% of private-sector research and development. The NAM is the powerful voice of the manufacturing community and the leading advocate for a policy agenda that helps manufacturers compete in the global economy and create jobs across the United States. For more information about the NAM or to follow us on Twitter and Facebook, please visit www.nam.org.
How a Chemical Manufacturer Made Testing Easier
Lubrizol, a specialty chemicals company, faced a challenge common to manufacturers in its sector: how do you test dozens or hundreds of new chemical formulations every year in a timely and cost-effective manner? The answer: better data analysis.
The Wickliffe, Ohio, company developed a virtual testing and data analytics system called Q.LIFE®, a solution so successful that the Innovation Research Interchange (the NAM’s innovation division) recognized it with the IRI Innovation Excellence Award for Digital and Technological Innovation. Here’s how they did it.
The problem: To develop its additives for engine oils, industrial lubricants, gasoline and other products, Lubrizol must run expensive tests that often took weeks if not months to complete.
- LIFE® changed the game, by providing more than 1,000 predictive models for different aspects of product development and deployment. For example, Q.LIFE® can help predict the outcome of those tests before they’re conducted, sometimes even eliminating the need to run a test in the first place.
- It also helps the company identify potential issues with raw materials before they end up in Lubrizol’s products.
- Last, as an added benefit, the system serves as an aid for training new employees on company processes.
Putting it to use: “Getting a handful of early adopters to start using it was key to making this a successful analytics system for years to come,” said Lubrizol Senior Manager of Data Science & Analytics Allison Rajakumar, one of the project’s pioneers.
- The team started by training a small group of employees in how to use Q.LIFE®. Those early users provided feedback on the system as it was being launched.
- As the use of the system grew, those employees acted as ambassadors for Q.LIFE® and trained other workers to use it, too.
Looking ahead: Lubrizol plans to expand Q.LIFE® to include more tools and to extend it to other areas of the business.
- The data science team is working with employees in other divisions, such as the company’s supply chain specialists, to develop models that will help optimize their processes as well.
Get involved: Has your company developed innovations to improve its operations and better serve its customers? If so, it might also be eligible for an IRI Innovation Excellence Award.
- Click here to learn more and start your nomination now. Submissions are due by Feb. 15.
How a Manufacturer Is Solving the Magnet Shortage

They say all you need is love, but in fact, you need a lot of magnets, too. Computers, appliances, electric generators and cars are powered by permanent magnet motors. Yet, most of the permanent magnets that make our modern life possible rely on rare earth materials, which are expensive, unsustainable and typically mined and processed in China.
To fix this bottleneck, Minneapolis-based Niron Magnetics is producing a new kind of magnet that uses two abundant raw materials: iron and nitrogen. By taking rare earths out of the equation, Niron’s Clean Earth Magnets® provide superior cost and supply chain stability to the countless manufacturers that depend on reliable access to high-powered magnets.
Why it matters: According to Niron, the demand for rare earths for critical magnets is outstripping the supply, and the problem is only getting worse.
- “When you look at the amount of magnets that are needed over the next 10 years, it’s triple the amount that are available today,” said Niron Magnetics CEO Jonathan Rowntree.
- “There’s only enough rare earth materials to double the amount of rare earth magnets manufactured every year. So there’s going to be this big imbalance later this decade. We’re well positioned to [meet] the shortfall of permanent magnets using iron nitride technology.”
The value proposition: Niron’s technology has several exciting upsides, according to company leaders.
- First, it relies on materials that are far more abundant and accessible than rare earths.
- Second, the supply chains for components like nitrogen and iron salts are very stable—and not centered in China.
- Finally, the production of a kilo of rare earth magnets generates 2,000 kilos of waste, according to Niron. By contrast, the production of Niron’s rare earth–free magnets is much more environmentally friendly.
- “Depending on which part you look at, whether it’s water or waste or greenhouse gas emissions, our production process is between 70% and 90% more efficient than the current rare earth processes today,” said Rowntree. “We’re excited about solving the environmental burden from the energy transition.”
Next steps: Niron is planning its first large-scale production facility in the United States, a 10,000-ton facility that it hopes will be operational by 2027.
- While its leaders are still considering different locations for the plant, they anticipate that the facility will ultimately result in 680 to 700 full-time jobs, not including the construction and infrastructure roles needed to build it.
- “We’re growing very quickly here in terms of our capability,” said Rowntree. “We’ve doubled the number of employees this year, and we will likely double that number again over the next several years.”
The bottom line: “There’s a growing awareness of critical materials and the rare earth supply challenges, and the risks posed by U.S. reliance on China to supply those magnets. But there isn’t a lot of awareness around the fact that there is an alternative solution,” said Rowntree. “There is alternative technology that we’re aggressively scaling and that will be commercially available by the end of this year.”