What’s Ahead for Manufacturing in 2024?

Getting a solid forecast of the year’s key issues in manufacturing can help your business prepare for anything. A panel of experts recently shared their 2024 outlook in the webinar “What’s Ahead for Manufacturing in 2024?” hosted by the Manufacturing Leadership Council, the NAM’s digital transformation arm.
They offered insights on the 2024 manufacturing economy, legislative climate, digital trends, resilience strategies and more.
Economic outlook: NAM Chief Economist Chad Moutray provided a manufacturing economic update.
Key takeaways:
- The NAM Q4 2023 Manufacturers’ Outlook Survey revealed that more than 66% of member companies have a positive economic outlook for 2024, yet opinions are mixed on whether there will be a recession.
- The top economic challenge this year will be the workforce, with the labor market cooling substantially but remaining tight, Moutray said.
- Private manufacturing construction spending is at an all-time high of $210 billion thanks to the production of semiconductors, electric vehicles and batteries, and general reshoring.
- Risks this year include geopolitical turmoil, slow global economic growth, cost pressures, talk of a recession and labor issues, among others.
Policy perspective: NAM Vice President of Domestic Policy Charles Crain gave an overview of the current climate in Washington, D.C., and the NAM’s legislative priorities.
Key takeaways:
- The NAM will continue its focus on tax policy following House passage of an NAM-supported bipartisan tax package that would reinstate three manufacturing-critical tax provisions.
- Manufacturing is facing a regulatory onslaught, with the average manufacturer paying $29,000 per employee per year due to unbalanced, burdensome regulations, according to a recent NAM-commissioned study.
- Artificial intelligence is a hot topic on Capitol Hill, with 60 AI-related bills introduced in Congress last year. The NAM is working to help policymakers understand the benefits of AI, including safety, worker training, product design and development, and efficiency.
Manufacturing 4.0 Trends: MLC Senior Content Director Penelope Brown offered a look at digital manufacturing trends on the horizon.
Key takeaways:
- Manufacturers can expect to see a broader adoption of existing AI applications, including predictive/preventative maintenance, improved processes and enhanced productivity.
- According to the MLC’s recent Smart Factories and Digital Production survey, 65% of manufacturers anticipate their level of M4.0 investment this year will stay the same as last year.
- Other trends to watch include the rise of global partnerships such as Catena-X and CESMII, digitized supply chains and reshoring.
Resilience perspective: Cooley Group President and CEO (and MLC Board of Governors Chair) Dan Dwight shared his approach to resilience in 2024 and the years to come.
Key takeaways:
- Business leaders should prioritize agility and adaptability, even if it means admitting to suboptimal results that require redirection.
- Resilience doesn’t mean perfection; it means learning from failures.
- AI and machine learning contribute to resilience by building out end-to-end visibility across an organization—from vendors to manufacturing operations to customers.
For additional details from these experts, watch “What’s Ahead for Manufacturing in 2024?”
March-In Proposal Undermines IP Rights, Hurts Manufacturers

The Biden administration’s proposal to invoke so-called “march-in” authority to seize the rights to patents developed in any part with federal funding would undermine the American innovation economy, the NAM told the federal government Tuesday.
What’s going on: A proposal put forth in December by the Biden administration would allow the government to seize private-sector patents for products it considers too costly.
Why it’s important: “Undermining manufacturers’ [intellectual property] rights would have sweeping ramifications for innovation in the United States and America’s world-leading innovation economy,” the NAM told the Biden administration.
- “In particular, start-ups and small businesses would bear the brunt of the drastic changes proposed by the administration, as … government march-in would disincentivize early-stage entrepreneurship and dissuade much-needed capital formation from outside investors.”
The background: The Bayh-Dole Act, passed in 1980, allows recipients of federal research dollars to license groundbreaking technologies to private-sector companies to commercialize them.
- “Prior to the act’s passage, the government held approximately 28,000 patents—yet fewer than 4% of those patents were licensed to the private sector. This is because private-sector participants viewed these patents as ‘contaminated by government funding,’” according to the NAM.
- Bayh-Dole includes a narrow “march-in” provision that allows the government to step in to ensure consumer access to certain products during times of crisis—but march-in “has never previously been used during the 44 years since the law’s enactment,” the NAM said.
- Allowing march-in based on the price of a product or technology “would hinder industry collaborations with research universities and laboratories across the country, stymieing manufacturers’ efforts to develop the products and technologies of the future and bring them to the public.”
What we’re doing: Last month, the NAM launched a seven-figure ad campaign opposing the proposal.
- The administration should “provide certainty to manufacturers and other stakeholders in the innovation economy by affirmatively and unequivocally withdrawing the proposal—and making clear that the administration will not implement any of its recommendations,” the NAM said.
The last word: “Undermining America’s world-leading patent system is a recipe for reduced innovation and significant economic damage, with a disproportionate impact on small manufacturers,” said NAM Vice President of Domestic Policy Charles Crain.
- “The administration’s march-in proposal would raise the spectre of government price controls on a wide range of technologies—fundamentally reshaping how life-changing innovation is developed, financed and commercialized in the United States. The administration must affirmatively and unequivocally withdraw this radical and flawed proposal.”
ICYMI: NAM Opposes Biden Administration’s Proposal to Undermine Manufacturers’ IP Rights
Washington, D.C. – Following the National Association of Manufacturers’ submission of comments opposing the Biden administration’s proposal that would allow the government to march in and seize the rights to groundbreaking innovations developed by manufacturers, NAM Vice President of Domestic Policy Charles Crain released the following statement:
“Undermining America’s world-leading patent system is a recipe for reduced innovation and significant economic damage, with a disproportionate impact on small manufacturers. The administration’s march-in proposal would raise the spectre of government price controls on a wide range of technologies—fundamentally reshaping how life-changing innovation is developed, financed and commercialized in the United States. The administration must affirmatively and unequivocally withdraw this radical and flawed proposal.”
The NAM’s comments on the proposal are available here. Key excerpts from the comments are below:
- The proposal contemplates an expansion of the Bayh-Dole Act’s march-in provision, which has never previously been used during the 44 years since the law’s enactment. This unlawful expansion of a 44-year-old statutory provision would prompt the government to exercise march-in rights to force patent licenses to private-sector inventions that are derived at least in part from federal funding. This price control measure would impact innovative companies of all kinds across the manufacturing sector.
- Undermining manufacturers’ IP rights would have sweeping ramifications for innovation in the United States and America’s world-leading innovation economy. In particular, start-ups and small businesses would bear the brunt of the drastic changes proposed by the administration, as the spectre of government march-in would disincentivize early-stage entrepreneurship and dissuade much-needed capital formation from outside investors.
- If the administration moves forward with the proposal, the unprecedented expansion and use of the Bayh-Dole Act’s march-in provision would impede R&D, investment and the commercialization of innovative technologies. It would cause significant market uncertainty as to current and future patent licenses that are derived in any part from federal funds—directly contradicting the intent and purpose of Bayh-Dole. And it would hinder industry collaborations with research universities and laboratories across the country, stymieing manufacturers’ efforts to develop the products and technologies of the future and bring them to the public.
- Courts have found that an agency violates the major questions doctrine on matters of significant economic importance when the agency cannot “point to clear congressional authorization for the power it claims.” The government’s ability to seize private-sector IP is undoubtedly a topic of vast economic and political significance; as discussed, America’s robust patent system lies at the heart of the innovation economy in the United States—and the proposal would threaten the financing of that innovation ecosystem and the economic viability of many of its key participants (including start-ups, entrepreneurs, small and medium-sized businesses, universities and more). The effects of the proposal would be felt in every state and every congressional district. Yet, the proposal cannot point to “clear congressional authorization” for including a price consideration in the government’s march-in analysis because it does not exist; as explained above, price is wholly absent from the Bayh-Dole Act’s text. More broadly, the act was enacted to support public–private partnerships and bolster the innovation economy in the United States—yet, the proposal would undermine and endanger American innovation. It is unlikely that Congress, in passing the Bayh-Dole Act, “could reasonably be understood to have granted” the administration the power to vitiate the primary goal of the act itself.
- The NAM respectfully encourages the administration to provide certainty to manufacturers and other stakeholders in the innovation economy by affirmatively and unequivocally withdrawing the proposal and making clear that the administration will not implement any of its recommendations. Abandoning and disclaiming the proposal’s attempts to impose price controls and undermine the Bayh-Dole Act will ensure that manufacturers in the United States can continue to lead the world in R&D and innovation—and continue to create and support well-paying jobs vital to the success of the U.S. economy.
-NAM-
The National Association of Manufacturers is the largest manufacturing association in the United States, representing small and large manufacturers in every industrial sector and in all 50 states. Manufacturing employs nearly 13 million men and women, contributes $2.85 trillion to the U.S. economy annually and accounts for 53% of private-sector research and development. The NAM is the powerful voice of the manufacturing community and the leading advocate for a policy agenda that helps manufacturers compete in the global economy and create jobs across the United States. For more information about the NAM or to follow us on Twitter and Facebook, please visit www.nam.org.
How a Chemical Manufacturer Made Testing Easier
Lubrizol, a specialty chemicals company, faced a challenge common to manufacturers in its sector: how do you test dozens or hundreds of new chemical formulations every year in a timely and cost-effective manner? The answer: better data analysis.
The Wickliffe, Ohio, company developed a virtual testing and data analytics system called Q.LIFE®, a solution so successful that the Innovation Research Interchange (the NAM’s innovation division) recognized it with the IRI Innovation Excellence Award for Digital and Technological Innovation. Here’s how they did it.
The problem: To develop its additives for engine oils, industrial lubricants, gasoline and other products, Lubrizol must run expensive tests that often took weeks if not months to complete.
- LIFE® changed the game, by providing more than 1,000 predictive models for different aspects of product development and deployment. For example, Q.LIFE® can help predict the outcome of those tests before they’re conducted, sometimes even eliminating the need to run a test in the first place.
- It also helps the company identify potential issues with raw materials before they end up in Lubrizol’s products.
- Last, as an added benefit, the system serves as an aid for training new employees on company processes.
Putting it to use: “Getting a handful of early adopters to start using it was key to making this a successful analytics system for years to come,” said Lubrizol Senior Manager of Data Science & Analytics Allison Rajakumar, one of the project’s pioneers.
- The team started by training a small group of employees in how to use Q.LIFE®. Those early users provided feedback on the system as it was being launched.
- As the use of the system grew, those employees acted as ambassadors for Q.LIFE® and trained other workers to use it, too.
Looking ahead: Lubrizol plans to expand Q.LIFE® to include more tools and to extend it to other areas of the business.
- The data science team is working with employees in other divisions, such as the company’s supply chain specialists, to develop models that will help optimize their processes as well.
Get involved: Has your company developed innovations to improve its operations and better serve its customers? If so, it might also be eligible for an IRI Innovation Excellence Award.
- Click here to learn more and start your nomination now. Submissions are due by Feb. 15.
How a Manufacturer Is Solving the Magnet Shortage

They say all you need is love, but in fact, you need a lot of magnets, too. Computers, appliances, electric generators and cars are powered by permanent magnet motors. Yet, most of the permanent magnets that make our modern life possible rely on rare earth materials, which are expensive, unsustainable and typically mined and processed in China.
To fix this bottleneck, Minneapolis-based Niron Magnetics is producing a new kind of magnet that uses two abundant raw materials: iron and nitrogen. By taking rare earths out of the equation, Niron’s Clean Earth Magnets® provide superior cost and supply chain stability to the countless manufacturers that depend on reliable access to high-powered magnets.
Why it matters: According to Niron, the demand for rare earths for critical magnets is outstripping the supply, and the problem is only getting worse.
- “When you look at the amount of magnets that are needed over the next 10 years, it’s triple the amount that are available today,” said Niron Magnetics CEO Jonathan Rowntree.
- “There’s only enough rare earth materials to double the amount of rare earth magnets manufactured every year. So there’s going to be this big imbalance later this decade. We’re well positioned to [meet] the shortfall of permanent magnets using iron nitride technology.”
The value proposition: Niron’s technology has several exciting upsides, according to company leaders.
- First, it relies on materials that are far more abundant and accessible than rare earths.
- Second, the supply chains for components like nitrogen and iron salts are very stable—and not centered in China.
- Finally, the production of a kilo of rare earth magnets generates 2,000 kilos of waste, according to Niron. By contrast, the production of Niron’s rare earth–free magnets is much more environmentally friendly.
- “Depending on which part you look at, whether it’s water or waste or greenhouse gas emissions, our production process is between 70% and 90% more efficient than the current rare earth processes today,” said Rowntree. “We’re excited about solving the environmental burden from the energy transition.”
Next steps: Niron is planning its first large-scale production facility in the United States, a 10,000-ton facility that it hopes will be operational by 2027.
- While its leaders are still considering different locations for the plant, they anticipate that the facility will ultimately result in 680 to 700 full-time jobs, not including the construction and infrastructure roles needed to build it.
- “We’re growing very quickly here in terms of our capability,” said Rowntree. “We’ve doubled the number of employees this year, and we will likely double that number again over the next several years.”
The bottom line: “There’s a growing awareness of critical materials and the rare earth supply challenges, and the risks posed by U.S. reliance on China to supply those magnets. But there isn’t a lot of awareness around the fact that there is an alternative solution,” said Rowntree. “There is alternative technology that we’re aggressively scaling and that will be commercially available by the end of this year.”
How Pioneer Service Solves the Retention Puzzle

For Pioneer Service President and Co-Owner Aneesa Muthana, having an engaged team is the key to solving the workforce retention puzzle. The Addison, Illinois–based, woman-owned company is among the many manufacturers that find retention, along with recruitment, to be top business challenges, as the NAM’s Manufacturers’ Outlook Survey shows. So how has Muthana gone about building such a team?
Where it all starts: For Muthana, meeting this challenge begins with upholding the company’s core values: integrity, diversity, leadership, outreach, stewardship, quality and learning.
- These words appear on the shop floor, and every job candidate who comes in for an interview receives a handout outlining their importance. “These are more than just pretty words on a wall,” said Muthana. “We chose these values as a team because they pinpoint our path to success, both financially and ethically.”
- “I give them a copy because I want them to understand the importance from the beginning,” said Muthana. “We want to plant the seed before they’re on our payroll that these are the expectations. Then it becomes fair to hold people accountable to them.”
Providing training opportunities: In keeping with its core values of stewardship and learning, Pioneer Service offers internal training opportunities for employees who express an interest.
- “We offer training to anyone who raises their hand, whether it be in safety or leadership,” said Muthana. “It can also be very technical training on the shop floor. We also provide GD&T training, including for our sales team.”
- GD&T, or geometric dimensioning and tolerancing, determines how parts fit together into an assembly to form a product.
- The benefit of having a salesperson learn about GD&T? “A salesperson would be able to look at a customer print confidently and feel comfortable talking to the customer without needing to have an engineer in the room,” Muthana pointed out.
Offering support: Pioneer Service established a chaplaincy program, which connects employees and their families undergoing hardships—such as caring for an elderly parent, grieving the loss of a loved one or dealing with a personal struggle—with a chaplain who can provide counseling and offer spiritual and emotional support. Muthana says that the chaplaincy program is open to any employee, regardless of religious background or preference.
- “The chaplain service is part of our team,” said Muthana. “We have one chaplain come in every week—one week a male and then the following week a female—who is available to meet with staff if needed.”
- Muthana says she used the service a few years ago when her son, who is in the military, came back from Afghanistan. Many of his friends did not.
- “As a parent, you feel grateful that your child survived, but also guilty for feeling that way because a lot of his friends didn’t come home. The chaplain service provided me someone to talk to because I couldn’t talk to my family, and I couldn’t talk to my staff,” she recalls. “I developed a strong relationship with the chaplain that I feel never would have happened if I didn’t look out for my staff and implemented the service.”
Job shadowing: When Muthana goes to a speaking event or conference, she sometimes takes one or two of her staff with her so they’re able to benefit from attending. It’s also a way for her to get to know her staff on a more personal level, outside of the formal workplace setting.
The last word: Muthana shared some advice for companies struggling with workforce retention:
- “Having an engaged team and workers only happens with a people-first mentality,” said Muthana. “When you take care of them, you become successful because you have an engaged team that has your back.”
- “It’s harder to make a profit than ever. The only way that we’re going to be successful is by having an engaged team.”
Go deeper: The Manufacturing Institute (the NAM’s workforce development and education affiliate) has many resources to help employers retain and develop their teams.
- Start with this study to learn how to build positive company culture and engage employees, explore strategies in boosting retention and employee engagement, delve into tips on attracting and retaining talent in rural vs. urban settings and check out the MI’s recent white paper on flexibility approaches for manufacturing production workers, a key tool to improving the employee experience.
- Pioneer Service’s approach to workplace needs exemplifies the benefits of focusing on the holistic frontline employee experience, which include higher retention, less absenteeism and greater engagement, according to a study conducted by the MI and PwC.
- Learn more about Women MAKE America and the 35×30 campaign, the MI’s initiatives to increase the number of women in manufacturing, tapping into this population to address persistent workforce shortages. Military-affiliated talent and second chance populations are great sources, too.
“March-In” Rights Would Harm Manufacturing, Economy

So-called “march-in” rights that would enable the federal government to seize manufacturers’ intellectual property are “a major threat to manufacturers in America,” according to a new seven-figure ad campaign launched by the NAM.
What’s going on: Last month, the Biden administration issued a proposal that would allow the government to take over privately held patents if those patents had been developed in part with federal research dollars.
The problem: Undermining companies’ IP rights would roll back the progress made under the Bayh-Dole Act, which allowed for commercialization of federally funded research and “unlocked all the inventions and discoveries that had been made in laboratories throughout the United States with the help of taxpayers’ money,” according to a recent op-ed in The Hill.
- Because the government is “inviting march-in petitions on every patented technology that benefited from even modest federal grants,” the proposal could “decimate American innovation [and] … stifle investment in climate change, sustainable agriculture, advanced computing, energy, medicines” and more, according to the op-ed writers, two former undersecretaries of commerce for intellectual property.
- In addition, the proposal is “putting American jobs at risk,” according to the NAM’s new ad.
The NAM says: “This radical new proposal is a major threat to manufacturers in America and counter to the president’s goals of growing the sector,” NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons said.
- “Empowering the government to march in and seize the rights to private-sector patents and technologies threatens American innovation and R&D, putting millions of well-paying manufacturing jobs at risk. Policymakers must protect manufacturers’ intellectual property rights and stop this government overreach.”
Manufacturers Launch Seven-Figure Ad Campaign Opposing Biden Administration’s March-In Proposal
Washington, D.C. – The National Association of Manufacturers has launched a seven-figure television and digital advertising campaign opposing the Biden Administration’s new proposal that would allow the government to march in and seize the rights to groundbreaking innovations developed by manufacturers.
“This radical new proposal is a major threat to manufacturers in America and counter to the president’s goals of growing the sector,” said NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons. “Empowering the government to march in and seize the rights to private-sector patents and technologies threatens American innovation and R&D, putting millions of well-paying manufacturing jobs at risk. Policymakers must protect manufacturers’ intellectual property rights and stop this government overreach.”
To view the latest television ad, click here.
-NAM-
The National Association of Manufacturers is the largest manufacturing association in the United States, representing small and large manufacturers in every industrial sector and in all 50 states. Manufacturing employs nearly 13 million men and women, contributes $2.75 trillion to the U.S. economy annually and accounts for 53% of private-sector research and development. The NAM is the powerful voice of the manufacturing community and the leading advocate for a policy agenda that helps manufacturers compete in the global economy and create jobs across the United States. For more information about the NAM or to follow us on Twitter and Facebook, please visit www.nam.org.
NAM Announces New Board Leadership
Seasoned Executives Take Helm at NAM as Policymakers Debate Competitiveness Issues for Manufacturing Industry
Washington, D.C. – The National Association of Manufacturers announced its Board of Directors has elected Johnson & Johnson Executive Vice President and Chief Technical Operations and Risk Officer Kathy Wengel as board chair and Rockwell Automation Chairman and CEO Blake Moret as vice chair.
“Building on the solid foundation left by Immediate Past Chair Jim Fitterling, chair and CEO of Dow, the NAM enters 2024 with continued successful results for our members, strong financial growth and forward momentum with Kathy as chair and Blake as vice chair. Their companies are at the forefront of modern manufacturing, representing the future of what our industry can accomplish,” said NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons. “Over the past often turbulent and unpredictable years, they both have used their platforms to champion our industry and help secure landmark legislation. In addition to being a strong global voice on supply chain reliability and manufacturing for the future, Kathy is a committed force for bringing more diversity into the industry through her support of the Manufacturing Institute’s Women MAKE America Initiative, in addition to her service on the MI Board.
“Blake represents some of the most exciting, high-tech elements of manufacturing, as a leader in the industrial automation and digital innovation space. His commitment to building the next-generation manufacturing workforce was evident when he worked to bring the NAM and MI’s Creators Wanted campaign to Rockwell’s Automation Fair in Chicago. Kathy and Blake’s counsel has been instrumental in shaping the NAM’s policy agenda and elevating the values that make America exceptional and keep manufacturing strong: free enterprise, competitiveness, individual liberty and equal opportunity.”
“The NAM is best in class for its ability to address important challenges facing the manufacturing industry—from bolstering supply chains to harnessing the power of new technology,” said Wengel. “It is a true privilege to take on this new responsibility as NAM board chair. As the association looks to the future, we will seize opportunities to advance policies that foster growth, promote sustainability and ensure the readiness and diversity of the modern workforce.”
“As our industry looks to the future, manufacturing plays a critical role in solving some of the greatest challenges facing society and is at the vital core of the American economy,” said Moret. “It is an honor to represent manufacturing across America as board vice chair of the NAM. I look forward to working with this influential and well-respected association to move our industry forward.”
Wengel serves on the Board of Directors of the MI, the workforce development and education affiliate of the NAM, and has been instrumental in bringing more women into manufacturing through the MI’s Women MAKE America Initiative. Moret has worked closely with Creators Wanted, the industry’s largest campaign to build the workforce of tomorrow and is a past chair of the MI.
The two leaders take on their new roles at a time when manufacturers are confronting growing regulatory hurdles from Washington, D.C., geopolitical instability and policy uncertainty; answering significant questions about the role of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence; and working to ramp up implementation of historic legislation like the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the CHIPS and Science Act.
The NAM Board of Directors guides the association’s leadership in policy advocacy, legal action, operational excellence, workforce development and news and insights. More than 200 manufacturing leaders serve on the NAM Board, helping advance an agenda that enhances manufacturing competitiveness and the industry’s ability to improve lives in the United States and around the world.
The new board leadership was elected at the September meeting of the NAM Board of Directors.
-NAM-
The National Association of Manufacturers is the largest manufacturing association in the United States, representing small and large manufacturers in every industrial sector and in all 50 states. Manufacturing employs nearly 13 million men and women, contributes $2.85 trillion to the U.S. economy annually and accounts for 53% of private-sector research and development. The NAM is the powerful voice of the manufacturing community and the leading advocate for a policy agenda that helps manufacturers compete in the global economy and create jobs across the United States. For more information about the NAM or to follow us on Twitter and Facebook, please visit www.nam.org.
From Moonshot to Reality: Syzygy Plasmonics’ Emissions-Free Reactor
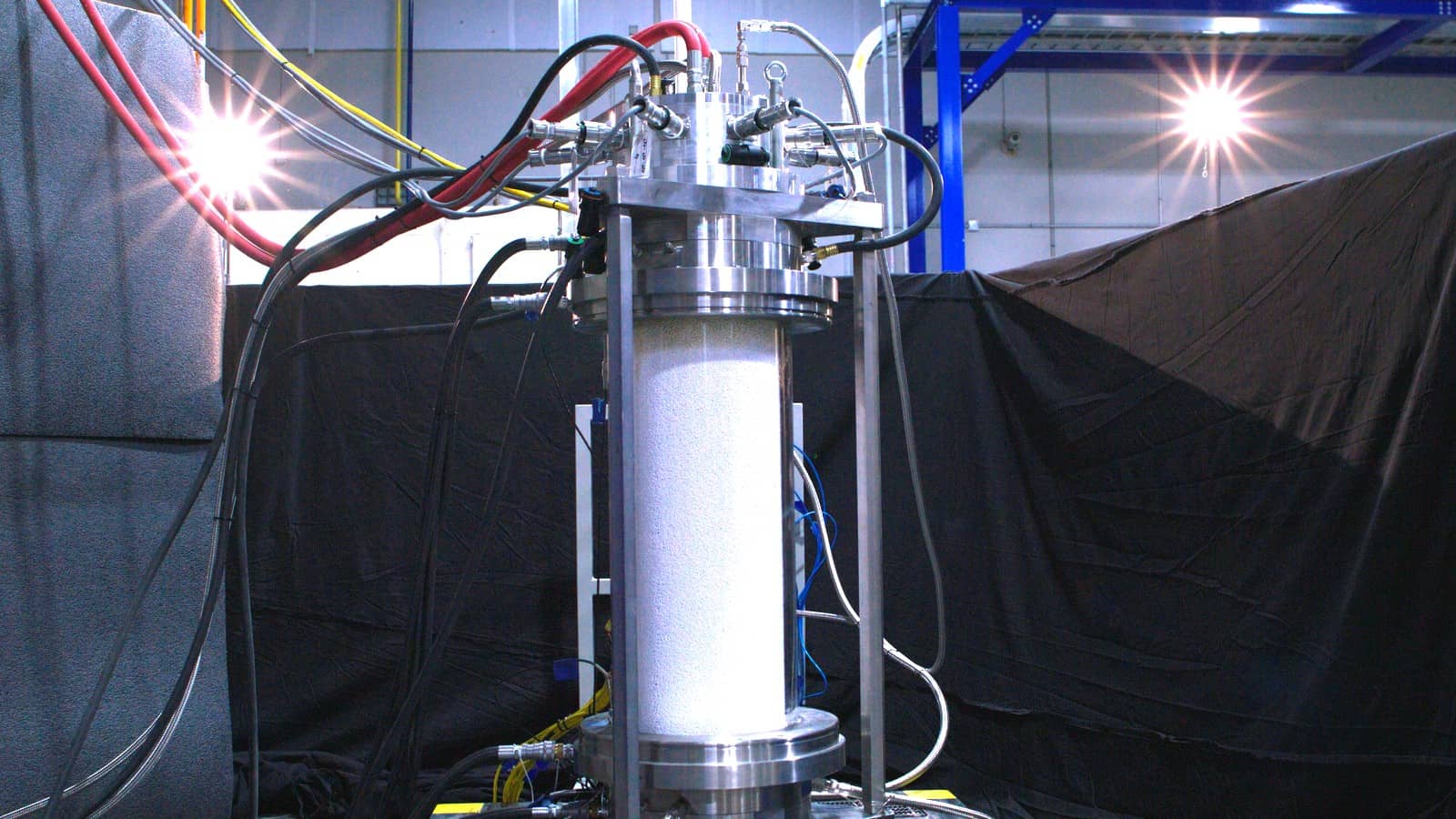

Syzygy Plasmonics is out to disrupt the $1 trillion chemical-manufacturing value chain.
The Houston-based startup, which bills itself as a “deep decarbonization company,” builds fully electric chemical reactors that are powered by light rather than traditional combustion.
That difference, CEO Trevor Best told us, is what will lead to disruption.
The big picture: “Chemical manufacturing is a foundation of modern human society,” Best pointed out. “With petroleum, natural gas and air, [companies] are able to create a wide variety of critical products,” from fuels and fertilizers to textiles and pharmaceuticals.
- “But today, it’s difficult to abate carbon emissions in chemical manufacturing,” he added. “That’s the problem Syzygy is working to solve.”
The backstory: In 2016, Best and Syzygy co-founder Dr. Suman Khatiwada “were looking for something disruptive” to invest in, Best said. “We reviewed lots of publications from major universities, and one day we happened to read about something happening at Rice University. This [idea] just would not die. We could not find a reason why it wouldn’t work, but no one else saw it.”
- After three decades of research, Rice researchers Naomi Halas and Peter Nordlander had developed a new kind of photocatalyst—a material that uses light to speed a chemical reaction—capable of “substantially lower[ing] the temperatures required for industrial-scale hydrogen production,” according to the university.
- “We quickly realized no one had ever made an industrial chemical reactor that could do that,” Best continued. He and Khatiwada contacted the researchers and eventually purchased the rights to the technology.
- Soon after, Syzygy was born.
Breaking records: In 2018, Syzygy successfully duplicated the Rice researchers’ experiment with a microreactor—but the result wasn’t as efficient at creating hydrogen as Best and Khatiwada wanted.
- They continued to scale up their testing, and by 2022, thanks to an advanced, large-cell reactor, the technology could produce hydrogen at 75% efficiency, surpassing the efficiency of traditional industrial chemical reactors.
- “We’re now on par with best-in-class electrolyzers” in terms of hydrogen production, Best said.
Affordable and emissions-free: One of the best things about Syzygy’s reactor? It produces no emissions, a characteristic the company believes will help it reach its goal of removing one gigaton of carbon dioxide emissions from the atmosphere by 2040.
- Another selling point is that the reactor is made with low-cost, readily available materials. Earlier this year, Syzygy unveiled a six-foot-tall reactor—made of “low-cost steel and glass,” according to Best—at its industrial demonstration plant just outside Houston, where it runs every day.
- Capable of multiple types of chemical reactions, the reactor has drawn interest from multiple companies wanting to deploy the technology in their own operations. Syzygy already has signed several contracts.
Up next: The company plans to bring three separate reactions to market at once in the near future.
- In addition to being emissions-free, the three reactions cost less than their traditional-combustion-powered counterparts, by between 20% and 45%, according to Syzygy.
The last word: Syzygy doesn’t envision many limits in its future, said Best.
- “We see this thing going global,” Best said. “We’re talking to customers all over the world. … [In the beginning,] I thought I was crazy. This was a moonshot. But it has exceeded all our expectations.”