Manufacturers Step into the Industrial Metaverse

What exactly is the industrial metaverse? While the term sounds like something straight out of a science fiction movie, it’s already being used by manufacturers in the here and now. Put simply, the industrial metaverse is a collection of technologies that can create an immersive virtual or virtual/physical industrial environment.
The metaverse will contain virtual replicas of everything from complete factories down to individual components and parts, powered by evolving digital technologies like AI and cloud computing. As the metaverse develops, users will be able to access it from any internet-connected device, such as a smartphone, laptop or tablet, or using virtual reality headsets.
According to a new report released by the Manufacturing Leadership Council, the NAM’s digital transformation division, and Deloitte, 92% of manufacturing executives say they are experimenting with or implementing at least one metaverse-related use case. On average, the surveyed executives say they are running more than six.
How is it used? Manufacturers are using industrial metaverse technologies in four common areas: production, supply chain oversight, customer service and talent management.
- Production: Manufacturers are simulating key processes in order to evaluate them, creating virtual prototypes of processes or systems and creating simulated factories to optimize factory layout and setup.
- Supply chain: Other manufacturers are using the metaverse to track products and raw materials and to collaborate with suppliers.
- Customer service: Companies are also creating virtual showrooms and product demonstrations, which attendees can visit without leaving their own homes or offices.
- Talent management: Lastly, other companies are experiment with using the metaverse for immersive training, virtual plant tours and virtual recruiting and onboarding.
What are the benefits? Executives report that each of these use cases comes with significant benefits, including cost reductions. Respondents also said metaverse applications have improved employee attraction and retention.
- Immersive customer experiences and virtual aftermarket services, such as equipment service and maintenance, have also led to increased revenue, according to the survey.
The challenges: While the industrial metaverse offers many promising benefits, manufacturers are still finding some challenges, including:
- The high cost of metaverse technology and the cybersecurity protections it requires;
- A lack of employees with the right skills, along with the steep learning curve for those who must be trained; and,
- Insufficient digital infrastructure and other resources.
The solution: The report suggests that manufacturers can find success in the metaverse by building a culture of innovation, establishing leadership support and starting small by investing in a digital technology foundation.
The last word: All in all, manufacturing executives are confident that the industrial metaverse will transform their operations. Learning to understand and use the metaverse will soon be essential for companies seeking a competitive future.
Download the full report, “Exploring the Industrial Metaverse,” to learn more.
How Novocure’s Anti-Cancer Device Extends Lives

Around 15,000 people are diagnosed every year in America with glioblastoma, a particularly aggressive form of brain cancer. At Novocure—a global oncology and medical device company with its North American flagship facility located in Portsmouth, New Hampshire—scientists and manufacturers have developed a device to revolutionize the way these tumors are treated.
The breakthrough: Novocure’s founder Yoram Palti developed an innovative treatment called Tumor Treating Fields therapy—an approach that uses electric fields to kill cancer cells while sparing healthy ones.
- For adult glioblastoma patients, the device, called Optune®, consists of wearable, portable adhesive arrays and an electric generator that can be carried in a bag.
- “Unhealthy cells and healthy cells have different properties,” said Frank Leonard, president, CNS Cancers U.S. at Novocure. “If you can create the right type of electric field, you can exert force and destroy cancer cells as they divide.”
Value added: Crucially, Tumor Treating Fields therapy is being studied together with other therapies, giving patients access to an optimal mix of treatments.
- “You get the best of both worlds with a device intervention and a drug intervention,” said Leonard. “Patients can wear this device consistently while using Temozolomide, which is the current standard of care chemotherapy agent used to treat glioblastoma.”
Low risk: Unlike drug therapies, which can present a range of adverse effects, Optune® has few side effects beyond mild-to-moderate skin irritation beneath the transducer arrays. As a result, patients can receive the treatment continuously for extended periods of time to attack cancer cells.
- “Typically, the limiting factor in treating cancer is dose-limiting toxicity—for example, you can only take one or two chemotherapies at the same time because they’re so toxic,” said Leonard.
Getting heard: The company’s device was featured in the award-winning short film “Rare Enough,” which tells the inspiring story of cancer survivor DJ Stewart and his journey in battling glioblastoma.
- Stewart is a Kansas City–based skateboarder who was first diagnosed with glioblastoma in 2019. Thanks, in part, to Tumor Treating Fields therapy, his life expectancy—once only 13 months—has been prolonged significantly. DJ now serves as a community outreach coordinator for the Head for the Cure Foundation.
Next steps: Novocure believes that Tumor Treating Fields therapy holds significant promise for other types of cancer as well. The company is developing additional wearable devices that could treat countless patients around the world.
- Lung cancer trials have shown promising results recently, and the company expects to learn more in the coming months from clinical trials involving ovarian cancer, metastases from lung cancer and pancreatic cancer.
- “We started working first in one of the rarer, yet most aggressive, forms of cancer. There are around 15,000 patients diagnosed with glioblastoma in the U.S. each year,” said Leonard. “But pre-clinical data suggests that Tumor Treating Fields can work with all different tumor types.”
A look to the future: Wearable anti-cancer devices offer an exciting new frontier in the fight against life-threatening diseases, and an important field where manufacturers can make an enormous difference.
- “In these really aggressive cancers, we still are making advances—and advanced devices that require sophisticated engineering and complex global manufacturing have a role to play,” said Leonard. “There’s a lot the manufacturing industry can do to improve the outcomes of patients, and they should be recognized for that work.”
PALIoT Takes on Supply Chain Challenges
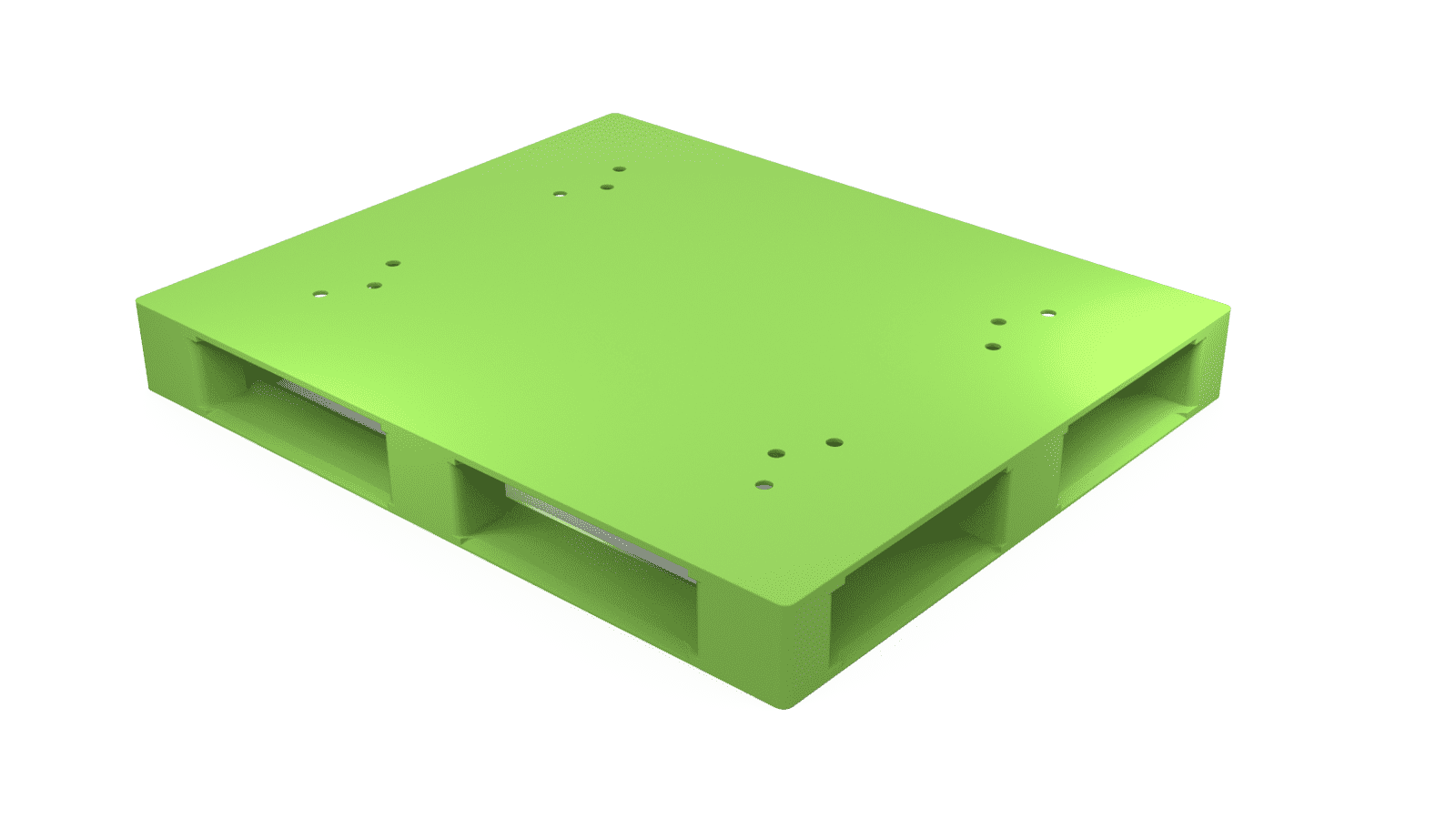
Supply chain problems, PALIoT Solutions is coming for you.
This fall, the New-York-state-based startup, whose name derives from a combination of “pallet” and “IoT,” will begin production of its smart shipping pallets. According to company leaders, these products will do nothing less than revolutionize the way food and goods are transported.
From vision to reality: PALIoT cofounders Paul Barry and Richard MacDonald envisioned pallets “whose positive impact on the environment keeps increasing as more of them are manufactured and deployed,” according to the firm’s website.
- To accomplish this feat, the pallets had to be both far lighter and more durable than typical pallets, which are made of wood and nails.
- After significant research and development, Barry and MacDonald came up with the solution: a polyurea-coated, engineered-plywood pallet that was 20 pounds lighter than its traditional peers and contained a proprietary sensor capable of instant communication with the cloud, making inventory tracking a cinch.
The “secret sauce”: “The ‘secret sauce’ is essentially a smart mesh network,” said Barry, who hails from Ireland and has an electrical engineering and investment banking background. “The PALIoT pallets in a shipment will all talk to each other, say, ‘Hey, I’m here.’ And [after shipping,] because they know they’ve been on a truck, they know they have to report all that valuable inventory and environmental data back to the cloud.”
- PALIoT, which will rent its pallets to customers using a per-pallet, pooling model (with an optional subscription service), acquired exclusive global use of the mist® Mesh Networking protocol. This ensures that communication is highly secure and battery sensitive at all times.
- The company estimates it will initially produce between 650,000 and 700,000 pallets a year in the first phase of the launch.
Savings for all: PALIoT’s groundbreaking sensors promise to save buyers both resources and money. 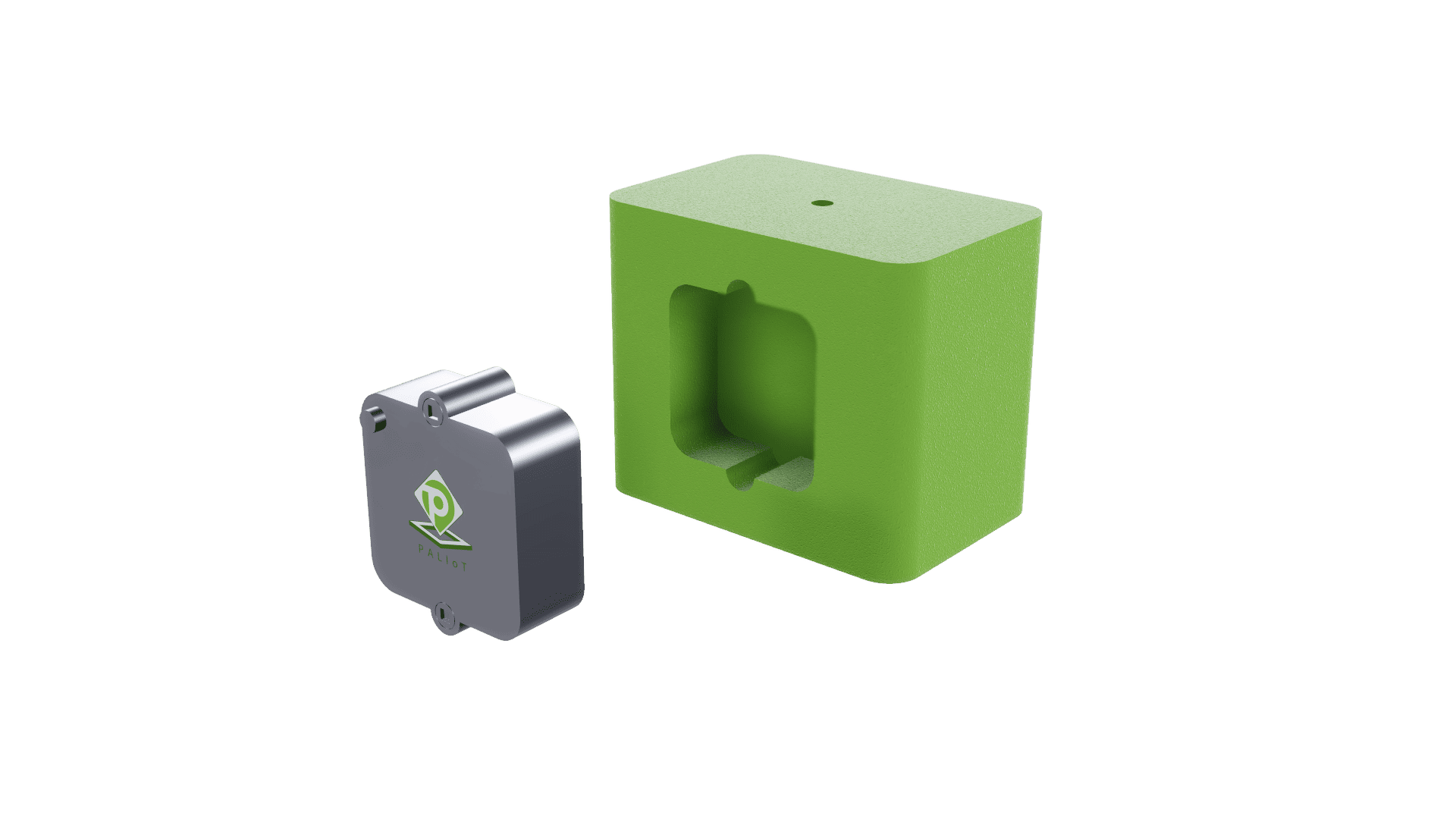
- “Food producers see tens of millions of dollars a year in food waste,” Barry said. With PALIoT technology, those producers will be able to track their perishable food shipments’ temperature and humidity conditions, viewing that information in the cloud so handlers can take swift action to cut down on spoilage.
- And because real-time asset protection is a PALIoT priority, the pallets will help companies cut down on theft and losses. As Barry put it, “If a pallet gets stolen, we will know where and when.”
A “smart” solution: Typical asset-embedded IoT sensors fail long before the assets themselves, making them impractical for longer-term use. Not so with PALIoT’s pallets, which can be used for a decade before they will need to be “retired and recycled,” according to Barry.
- “How can you justify having an expensive piece of hardware with a battery that needs replacing every few years?” he continued. “Using a combination of communications technologies, we’ve been able to solve the key problems of battery life and cost for large-scale asset-pooling companies.”
What’s next: Having recently relocated its manufacturing operations from Colorado to just outside Rochester, New York, PALIoT has its sights set on doing business with the dairy farms of the Northeast. It also plans to expand its manufacturing footprint across the U.S.
- “Demand is not the issue,” Barry told us. ”People just want a better solution, and we think this is it.”
How Can Companies Boost Morale?

After a global pandemic and amid considerable economic strain, worker morale may not be everything a company hopes. So what can leaders do to boost communication and restore a sense of excitement and purpose?
The Innovation Research Interchange—the NAM’s innovation division—recently published a whitepaper on morale building, drawing on copious existing research as well as consultations with leaders in a range of industries (from aerospace to consumer goods). Here are some of its key recommendations.
Senior leaders in the trenches: The best way to understand company morale (or its absence) is to go looking for it. In one notable case, FM Global Chief Science Officer Lou Gritzo spent a day working in each company lab, so he could understand where communication and cooperation needed improvement.
- Thanks to this experiment, Gritzo was able to “open lines of communication up and down the organization,” according to the IRI, leading to both an improved flow of information and greater comfort among lab staff in making independent decisions.
- “For others looking to try their hand at being a (not so) undercover boss, [Gritzo] recommends setting out rules of the road in advance,” the IRI paper notes. “The goal is to create a dialogue, not make guarantees that things will change. The change comes from the relationships built.”
Support for midlevel managers: Many participants in the IRI’s roundtables and interviews agreed that midlevel managers have only become more crucial in recent years—which explains why these managers are often very stressed.
- Amid the pressures of the pandemic, companies began offering more support and coaching for middle managers, according to earlier IRI research.
- One organization studied by the IRI and its research partner, Babson College, brought in coaches to work with managers—but not just for one-off sessions. “The external coaches were brought in multiple times during a one-year period in order to observe leadership styles and gave feedback openly,” which led to improved communication and greater autonomy among the managers.
Everyone an innovator: Another way to boost morale is to make sure great ideas are always recognized, no matter who comes up with them.
- At ICL Group, leaders devised a novel way to encourage innovative thinking: “an online platform that allowed anyone at ICL Group to propose an idea, have it reviewed by management, voted on by frontline staff and assigned to the appropriate team for implementation.”
- The platform has proved very popular, according to one senior leader, who said, “Everybody has just been blown away by how many ideas people have entered and [how many employees] continue to do it.”
Read the whole thing: Check out many more useful details and expert advice in the full whitepaper, which you can find here.
How Manufacturing 4.0 Got Its Name—and Why It Matters

Flashback to 2015: “Hamilton” debuted on Broadway, millennials surpassed baby boomers as the largest U.S. generation and the term “Industry 4.0” was gaining traction in manufacturing circles. It was also when the Manufacturing Leadership Council created a conceptual framework called “Manufacturing 4.0.”
So what is the difference between Industry 4.0 and Manufacturing 4.0? While the terms may not sound all that distinct from each other, Manufacturing 4.0 represents the MLC’s commitment to a far-sighted, holistic approach to manufacturing’s tech-enabled metamorphosis—one that has served it well in over the past eight years.
The background: The 4.0 movement started in Germany in 2011 when the German ministries for education, research, economic affairs and energy developed a strategic initiative that would push forward the digital transformation of industrial manufacturing.
- They named this initiative Industrie 4.0. It featured an action plan that combined policy initiatives, public–private funding, strategies for technology implementation and the identification of business drivers and barriers.
The difference: For the MLC and its members, Manufacturing 4.0 is made up of transformations in three different arenas: technology, organization and leadership.
- Contrast this with Industry 4.0, which covers only technology topics—specifically nine pillars of technological innovation, which include autonomous robots, big data, cloud computing, IoT, cybersecurity, systems integration, simulation, AR/VR and additive manufacturing.
- “MLC, of course, covers all of these technologies, but, importantly, adds the dimensions of organizational and leadership change as part of its perspective on manufacturing’s digital transformation,” says David R. Brousell, the MLC’s founder, vice president and executive director.
MLC in action: While the MLC does provide member resources that focus on specific technologies and their uses in manufacturing operations, it also covers topics such as how leaders can prepare their workforce for digital transformation, how organizations should be structured to make business decisions based on manufacturing data and how leaders can ensure they set their teams up for digital success.
- Additionally, the annual Manufacturing Leadership Awards recognize not only high-performing digital manufacturing projects but also outstanding individuals who demonstrate both technological understanding and strong personal leadership.
M4.0’s continued evolution: Today, the MLC continues to use Manufacturing 4.0 as the overarching framework for its member companies’ activities.
- Its influence is apparent in the MLC’s annual Critical Issues Agenda, a member-created list of key business drivers and enablers of digital manufacturing.
- The agenda covers technological advances like smart factories and data analytics, alongside the organizational ecosystems that put such advances into operation—from the leaders who direct them to the cultures that make them succeed.
The Future of M4.0: As the MLC gets ready to set its 2023–2024 Critical Issues Agenda, it will continue to take a holistic approach to the technological changes sweeping the industry by recognizing the importance of people in making those transformations happen.
Go deeper: You can learn more about Manufacturing 4.0 by downloading the MLC’s white paper, Manufacturing in 2030: The Next Phase of Digital Evolution; reading a recent report, The Future of Industrial AI in Manufacturing; or attending its Aug. 30 virtual Executive Interview, Shifting from Disruption to Growth.
A Homegrown Solution: Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Makes Printed Circuit Boards
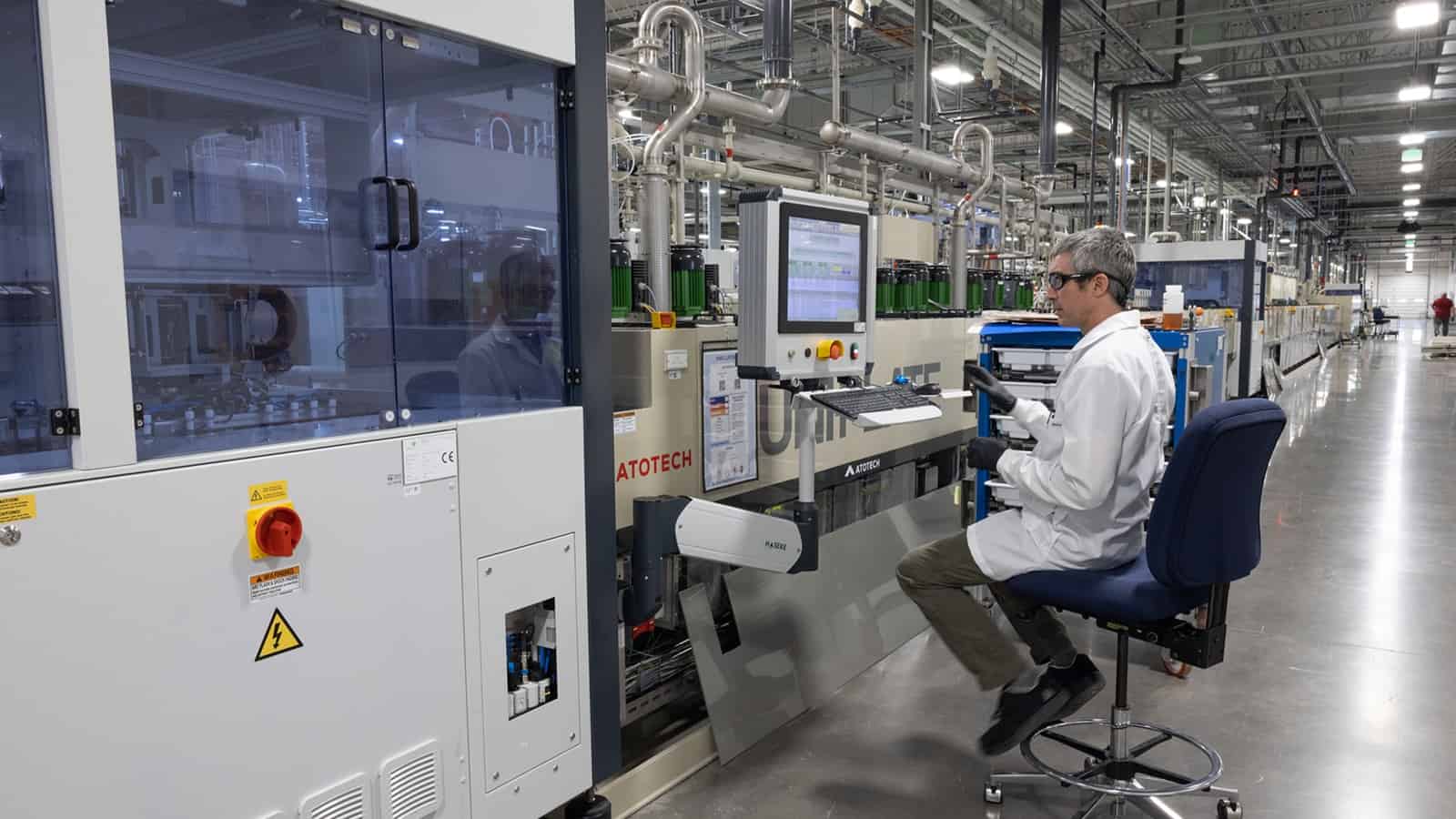

With one of its key components—printed circuit boards—in short supply, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories chose the proactive solution: it would begin making them itself. Now that its new factory is up and running, SEL is receiving unexpectedly keen interest from other companies, and considering ramping up production for outside sales.
Fixing a supply chain problem: The Pullman, Washington–based electric power system protection solution manufacturer began manufacturing PCBs at its new $100 million, 162,000-square-foot factory in Moscow, Idaho, back in March.
- “Printed circuit boards take electronic components and interconnect them so they can interact with each other,” SEL CEO David Whitehead said. “Without them, you can forget about AI, forget about your cell phones—they’re in just about any electronic device.”
- The Moscow factory is running at about 25% capacity. When it reaches full production later this year, it will be one of the top PCB manufacturers in the U.S., according to Whitehead.
Domestic and accessible: The PCB “is a critical component that goes into our devices,” Whitehead continued. “Now, instead of sourcing PCBs from around the U.S., we can produce them ourselves.”
- The Moscow facility—which only produces the circuit boards for SEL—has increased the company’s supply chain resiliency and sped up its output, Whitehead told us. “Now, in a handful of days after designing a printed circuit board for a product, our engineers are in their labs testing it. It’s a big win for us.”
- Nearly half of manufacturers in the U.S.—44.9%—cite supply chain hurdles as one of their top business challenges, according to the NAM’s Q2 2023 Manufacturers’ Outlook Survey.
Self-funded and viable: SEL funded 100% of the facility’s construction costs, and it will have paid for itself in two to three years, Whitehead said.
- “I think that’s really a big deal for not only taxpayers but the local community generally,” he said. State and local governments “can take the funds [they didn’t use on us] and invest” elsewhere.
A good neighbor: The Moscow plant—which features a fume scrubber system that exceeds Environmental Protection Agency standards for volatile organic compounds—also uses a “zero-liquid discharge water treatment system that recycles and reuses all the water used to manufacture the printed circuit boards,” Whitehead said.
- A comparable factory would use about 90,000 gallons of water each day of production, while SEL uses about 500 to 600 gallons—the equivalent of only a few households’ daily usage, according to Whitehead. Most of that is for worker needs (drinking water and restrooms).
- The company also reclaims and reuses metals, such as tin, silver and gold, that are used in the production process.
- “We are very environmentally conscious about how we produce these boards,” Whitehead said.
What’s next? Since the facility began production, SEL has gotten numerous inquiries from other manufacturers interested in buying the PCBs. The company is likely to oblige them soon.
- “This is our next opportunity,” Whitehead said of producing boards for other manufacturers. “We love being vertically integrated, building as much as we can close to where we’re going to use the products. … As we get better at it for our own consumption, I can see us expanding it.”
How Wabash Made Innovation Its Mission
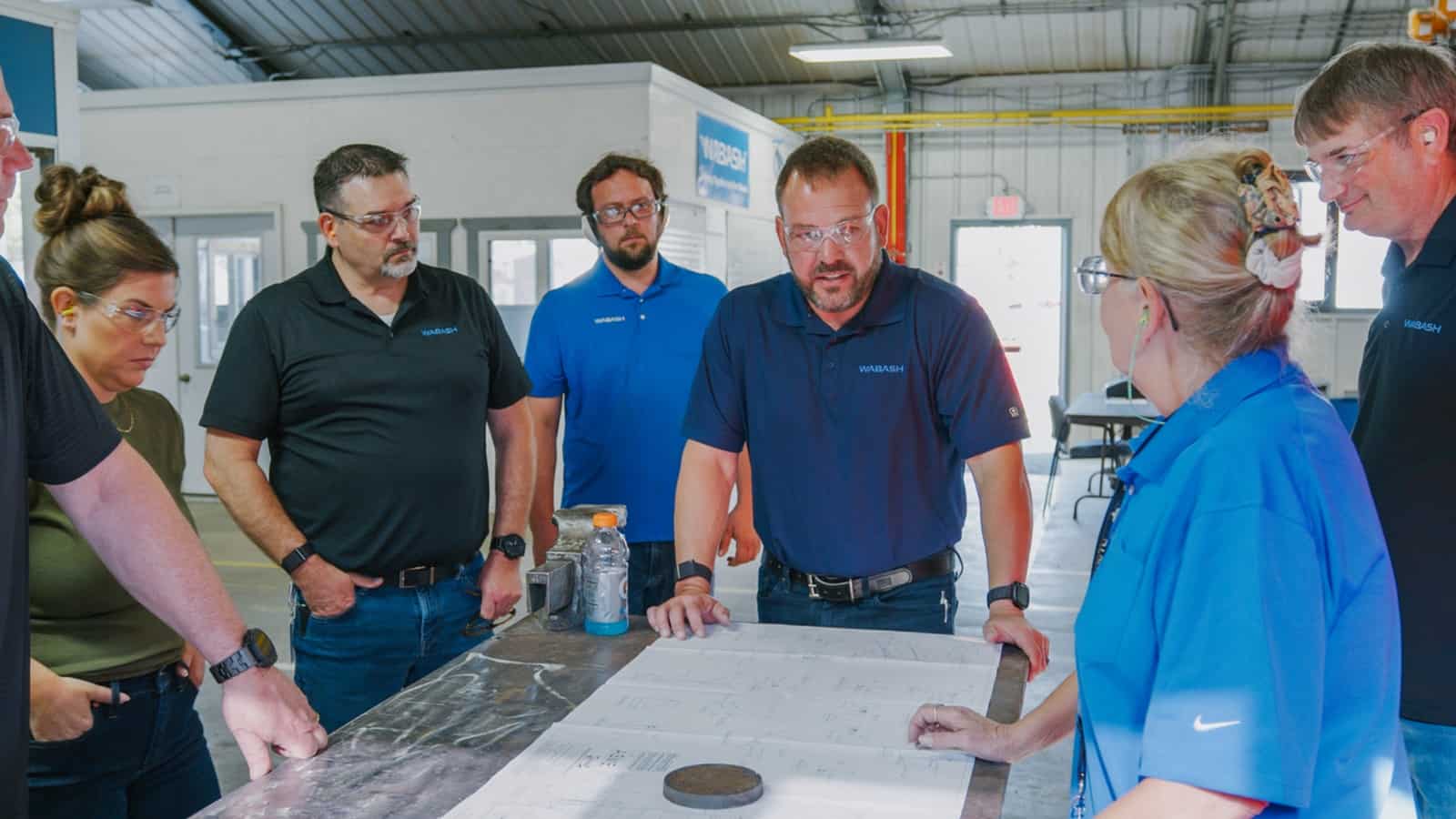

Innovation isn’t just one of many priorities at transportation systems manufacturer Wabash—it’s at the center of everything. Instead of having a traditional R&D function in the product development department, the company has reorganized its hierarchy so that innovation is considered in every major decision, from hiring to investments and more.
“It’s not possible to have innovation siloed in the engineering world; that wouldn’t allow us to achieve the scale of innovation that customers need,” President and CEO Brent Yeagy said.
As the manufacturing supply chain becomes increasingly intricate in a complex world, Wabash is staying ahead of the game. In a recent interview, Yeagy explained how the company does it.
The big picture: This “full reimagining” of the company occurred in response to broad forces reshaping the manufacturing industry, said Yeagy.
- Within the past decade, e-commerce has totally disrupted the logistics model of the previous 30 years, he pointed out.
- Meanwhile, digital technology has enhanced the speed and precision of the industry, which has also increased the complexity of its logistics needs.
- On top of that, the pandemic altered manufacturers’ thinking about lean inventories, lead times and the domestic supply chain infrastructure, sparking a system-wide transformation that isn’t over yet.
- And that’s all before we get to the possibilities of artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles, and new sources of clean energy—all of which could bring profound and unpredictable changes to the industry.
The response: Watching these changes unfold, Yeagy and his team knew they had to take dramatic steps to keep up.
- “We restructured the entire organization away from standalone divisions,” prioritizing collaboration instead, Yeagy said. This involved “aggregating R&D and business development,” which had previously been spread out over 11 different departments.
- This shift also reflected a change in the company’s philosophy. Innovation could no longer be incremental, Yeagy determined, but had to be audacious.
The internal system: Such advances are only possible if the company has a flexible, fast-moving core of innovators who are always looking for the next opportunity, Yeagy told us.
- Instead of creating an innovation strategy that “sits on a shelf” for a year or more, Wabash updates its strategy on a weekly or monthly basis.
- While the company’s R&D and corporate development teams have strict objectives, they can also challenge the strategic direction and introduce fresh ideas—such as new technologies that might give the company an edge.
- This system also requires the right people for the job. Team members must have not only the technical qualifications for the work, but also the capacity to trust, collaborate and be vulnerable when sharing ideas, Yeagy said.
The successes: The company’s new structure has led to industry-leading innovations like Wabash’s subscription model, which allows clients to “subscribe” to a certain level of fleet capacity, instead of managing a fleet of trucks themselves.
- Wabash manages the fleet and maintenance, Yeagy explained, guaranteeing a certain capacity every day to its customers, while offering a range of rental models to suit their needs.
- In another victory for its innovative corporate development team, Wabash found a swift solution when it discovered it didn’t have sufficient distribution capabilities for aftermarket parts. It created a joint venture with a competitor company that had ample warehouse space across the country—going from the idea stage to nationwide operations in a mere six months.
Military influence: Yeagy’s service in the Navy shaped his leadership throughout the company’s transformation, he told us.
- “The military is based on a mission orientation,” he explained. “If everyone understands where we are supposed to go and why, it allows them to be agile and overcome obstacles” in the field, where the unpredictable happens.
- “Officers live to complete the mission by taking care of their people, preparing them mentally, physically, operationally,” and then allowing them to operate on their own. “We have to do that too,” he concluded.
A word of advice: Yeagy advises manufacturing leaders that truly experimental teams require “a safe place to fail and learn how to be comfortable with failure.” He admits that “It’s very hard to take a manufacturing company that doesn’t want to fail, and to teach them,” so leaders must strive to be “immensely” empathetic. It’s clear from speaking to Yeagy that this is his top priority.
Wisconsin Manufacturers & Commerce Honored with 2023 Leadership Award from Conference of State Manufacturers Associations
Bluffton, S.C. – Today, the Wisconsin Manufacturers & Commerce was honored with the 2023 Leadership Award from the Conference of State Manufacturers Associations, whose members also serve as the National Association of Manufacturers’ official state partners and drive manufacturers’ priorities on state issues, mobilize local communities and help move federal policy from the ground up in all 50 states and Puerto Rico. WMC was recognized for their work to attract and maintain the manufacturing workforce.
“We congratulate Kurt Bauer and the entire team at WMC for their incredible work this year to not only educate the next generation of manufacturing workers in Wisconsin, but also engage the business community at large to help spur investment in the state,” said Utah Manufacturers Association President and CEO, NAM board member and COSMA Chair Todd Bingham. “Their work shows the impact that we can all have to help make the United States the top destination in the world for manufacturing investment.”
The Leadership Award recognizes the achievement of a state manufacturing association that has developed impactful initiatives to support manufacturers and strengthen manufacturing in their state. Some of the initiatives that set WMC apart were their Coolest Thing Made in Wisconsin and Business World, which teach young people about entrepreneurship and free enterprise and promote manufacturing job opportunities in the state. Additionally, as part of WMC’s official mission to make Wisconsin the best place for business, the Future Wisconsin Project brings together diverse interest groups to identify and address the state’s long-term economic challenges and opportunities, including solutions to workforce challenges.
“The work of WMC to inspire the workforce of the future is a prime example of what’s needed to address the critical challenges that our sector faces today,” said NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons. “Under Kurt Bauer’s leadership, the WMC is advancing the solutions needed to make manufacturers more competitive and ensure manufacturing remains a key driver of Wisconsin’s economy.
-NAM-
The National Association of Manufacturers is the largest manufacturing association in the United States, representing small and large manufacturers in every industrial sector and in all 50 states. Manufacturing employs nearly 13 million men and women, contributes $2.91 trillion to the U.S. economy annually and accounts for 55% of private-sector research and development. The NAM is the powerful voice of the manufacturing community and the leading advocate for a policy agenda that helps manufacturers compete in the global economy and create jobs across the United States. For more information about the NAM or to follow us on Twitter and Facebook, please visit www.nam.org.
Workforce Retention Begins with Culture at Ketchie
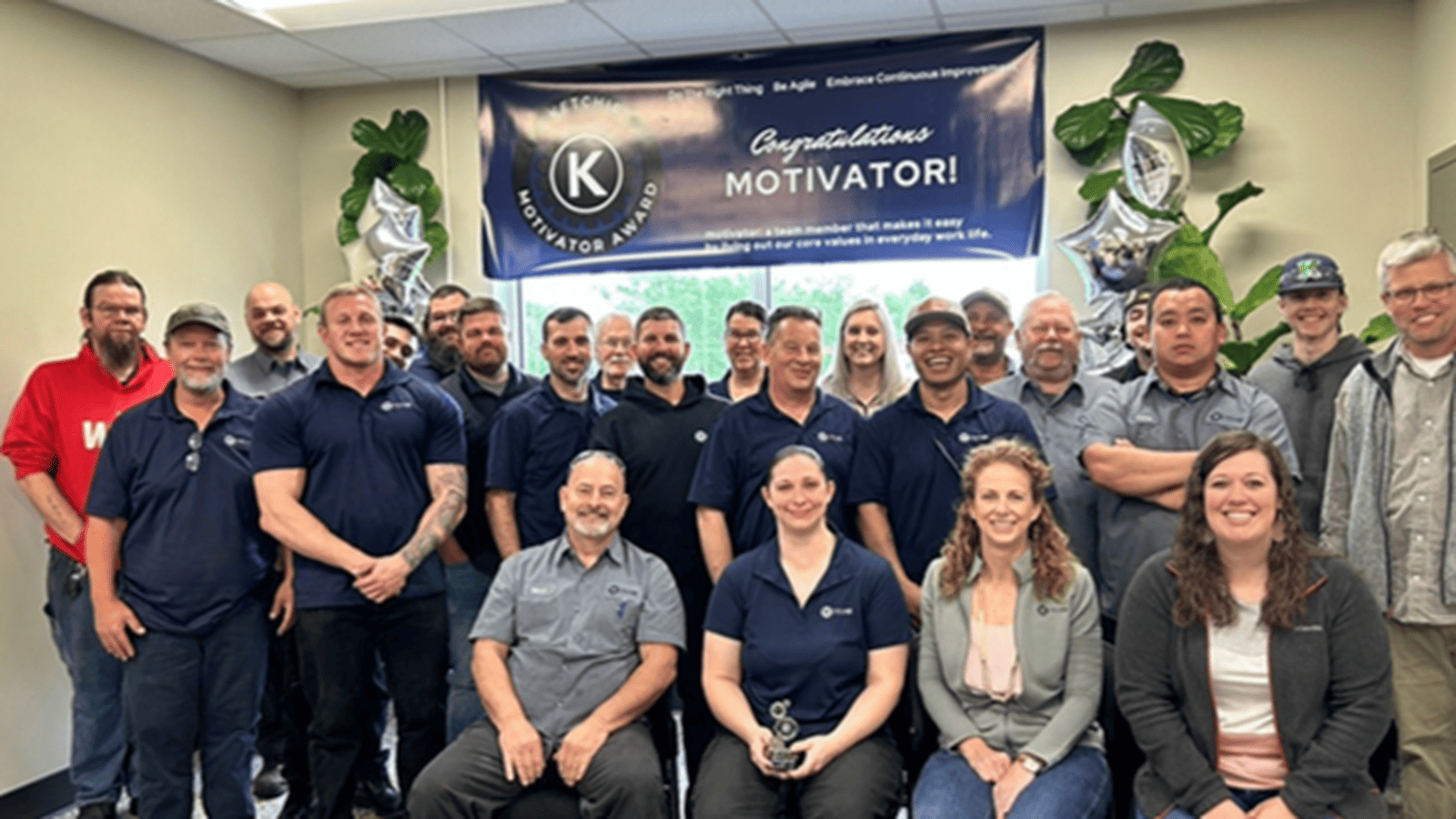

For Ketchie President and Owner Courtney Silver, retention all starts with culture. “I’m really happy to be here” is a phrase she hears often on her shop floor—and it tells her that the work culture at her company is in good shape.
- “A culture of empowerment that’s built on trust really fuels our team I think,” said Silver, who is the chair of the NAM’s Small and Medium Manufacturers Group. “They find so much dignity and purpose in fulfilling our mission here at Ketchie.”
Maintaining a high-performing, motivated and engaged workforce is a top priority for the third-generation precision machine shop in Concord, North Carolina, and Silver has implemented a number of strategies to keep it that way.
Team recognition: Every Wednesday, during Ketchie’s shift meeting, employees have the opportunity to recognize their team members for any achievement, big or small.
- “Recognition can be about anything,” says Silver. “It can be ‘Fred over there was able to cut five minutes of cycle time off this particular part because he changed the process’ or ‘Mary saved us money by switching out some tooling.’ We then post the feedback in the break room and email it out to the entire organization.”
- “There are so many things that can go wrong in manufacturing just trying to get a part out the door, and this is an opportunity to think about all the amazing things we’re doing,” she explained.
Silver also posts worker productivity charts every week. If workers meet their productivity goals and their indirect time goals, they get performance points, which are redeemable for gift cards.
- “I think people want to know if they’re on a winning team,” Silver said. “If you’re winning, it feels good. We’re all on the bus going in the same direction.”
Motivator Award: Each year, employees can also nominate a peer for the “Motivator Award,” which goes to the employee who best exemplifies Ketchie’s core values: to do the right thing, be agile and embrace continuous improvement.
- To honor the winner, Silver puts together a tribute video of team members sharing their thoughts about the employee and hosts a company brunch in celebration (to which the employee’s family is invited).
- “The winner also receives their own special parking spot, an extra day of vacation and a $1,000 gift certificate to the Marriott to take vacation with their family,” says Silver.
- “The team member that won the award last year had tears in his eyes, so I know that it’s been really impactful,” she continued.
Community service: Ketchie’s employees are passionate about giving back to the community. Through service projects, Ketchie supports the Boys & Girls Clubs of America as well as Cooperative Christian Ministry, which offers programs that relieve hunger and food insecurity and address homelessness and housing costs.
Opportunity Knocks: Silver isn’t only working to retain and support current employees, but also to train and mold the young people who will be tomorrow’s machinists.
- This year, Silver started an internship program for high school students named Opportunity Knocks. It allows students to shadow experienced machinists in factory environments while earning school credit.
- The interns go through a curriculum created by Edgerton Gear, Inc., called Craftsman with Character, a 16-week course that helps students explore the role of character in a professional trades environment. Silver said the course, which includes leadership and manufacturing-focused exercises, is taught at Ketchie four days a week in two-hour sessions. Three days of the week are job shadowing machinists on the shop floor, and one day is in a classroom setting at the shop discussing character traits and soft skills. The conversations lean on discovering what’s important in life and what might make them happy.
- “They absolutely love these high schoolers,” said Silver about the two mentors at Ketchie, who each have more than 30 years’ experience. “It gives them an opportunity to share their entire work career: what they’re doing, experiences learned along the way. It’s been neat to see.”
Investing in technology: Silver knows her team wants to work for a company that’s growing and investing in technology. She recently purchased a machine-tending collaborative robot, which takes over machinists’ “least favorite” part of the job—changing parts while the machines run.
- “I interviewed somebody recently who said to me in the interview, ‘It’s really good to see that you want to grow and that you’re making these big investments,’” said Silver. “You’re buying new technology that excites them. They want to be part of that mission and growth.”
The last word: Silver shared some advice for companies that might be struggling with workforce retention.
- “Use employee surveys, focus groups or roundtable discussions to see what you need to do or should do. Everyone wants to be heard. It’s important to listen.”
The NAM’s workforce development and education affiliate, the Manufacturing Institute, has many initiatives to help employers retain and develop their teams. For a deeper dive, check out this study by the MI on improving retention and employee engagement. The MI will also explore retention challenges and solutions at its Workforce Summit in Atlanta on Oct. 16–18. Click here for more information.
Committing to Net-Zero Emissions: Thermo Fisher Takes Action

Thermo Fisher Scientific of Waltham, Massachusetts, has made a big commitment to the environment, as well as to its customers and partners: to achieve net-zero emissions across its entire value chain by 2050.
By 2026, thanks to virtual power purchase agreements, all of the company’s current U.S. sites will be running on 100% renewable electricity.
And that’s not all. Last December, Thermo Fisher, a global life sciences leader, announced its intention to slash Scope 1 and 2 emissions—those generated directly by the company and by energy the company has purchased, respectively—by more than 50% by 2030 (from a 2018 baseline). At the end of 2022, the company had already cut emissions by 25%, putting it ahead of schedule.
Environmental sustainability: Thermo Fisher signed on to the Business Ambition for 1.5˚C campaign, which urges companies to reduce emissions sufficiently to cap the global temperature increase at 1.5 degrees Celsius. The campaign is led by the Science Based Targets initiative—the leading global standard setter for private companies’ climate goals—in partnership with the United Nations Global Compact and the We Mean Business Coalition.
- To reach that goal, global emissions must be halved before 2030, and the world must get to net-zero emissions before 2050, according to the SBTi.
- It’s a significant effort, but one Thermo Fisher—which is among the first companies in its industry to have its near- and long-term net-zero goals validated by the SBTi—is glad to take on.
- “Our commitment to the environment is deeply rooted in our mission to enable our customers to make the world healthier, cleaner and safer,” said Meron Mathias, vice president of Corporate Social Responsibility & Sustainability for Thermo Fisher Scientific. “By championing a healthy planet that sustains human health and natural resources, we can build a brighter future for generations to come.”
Making progress: While transitioning completely away from fossil fuels for its operations would require “clean energy technologies that aren’t yet available,” Mathias said the company has made significant recent strides in decreasing its carbon footprint. In 2022 alone, Thermo Fisher:
- Transitioned 20 of its facilities across the globe to operate without the use of fossil fuels (defined as at least 99% of total energy consumed from renewable sources).
- Powered 150 of its sites worldwide solely with renewables.
- Saw 13% of its suppliers (by spend, an industry metric) set a science-based target and another 10% commit to set a science-based target.
Key drivers of this progress include:
- Signing contracts to add 900,000 megawatt hours of renewable electricity to the electrical grid through power purchasing agreements (roughly the amount of electricity needed to power 82,000 average modern homes for a year).
- Purchasing enough wind and solar electricity to fuel all current U.S. sites by 2026, via virtual power purchasing agreements.
- Setting a Scope 3 emissions target to have 90% of its suppliers by spend set science-based targets by 2027.
All hands on deck: Thermo Fisher is also accelerating progress toward its sustainability goals in large part thanks to the company’s Practical Process Improvement Business System, according to Mathias.
- “A lot of our early wins in environmental sustainability have been through PPI,” she said. “For example, somebody seeing waste in the system, or identifying an opportunity to tweak something to make it better for the environment and customers. Our teams are empowered to find a better way every day—for our customers, our business and our planet.”
