Sustainability Is a Top Manufacturer Priority, Survey Shows

Manufacturers are pursuing sustainability like never before.
That’s according to recent polling conducted by the Manufacturing Leadership Council, the NAM’s digital transformation division. The annual Sustainability and the Circular Economy research survey seeks to determine the progress made in sustainable manufacturing.
Competitiveness: There has been a surge in the number of manufacturing executives who view sustainability as critical to the future of their businesses.
- 58% of respondents in 2022 believe sustainability is essential to future competitiveness compared to 38% in 2021.
- 68% of executives say they are implementing extensive, corporate-wide sustainability strategies. That’s up from just 39% in 2019.
What’s driving change: The motivations go beyond regulatory compliance and cost savings.
- 78% say sustainability is about better alignment with corporate values.
- 68% believe in creating a cleaner, healthier environment.
- 66% seek to improve company reputation with customers and investors.
Top corporate goals: More than half of survey respondents reported having specific sustainability goals and metrics across almost all key functions in the company.
- Goals were most apparent in manufacturing and production (79%), supply chain (69%) and product design and development (67%).
- Additional goals were cited in transportation and logistics (56%) and partner compliance (51%).
Energy efficiency is No. 1: The primary sustainability focus of manufacturers, according to survey results, is energy efficiency and reduction, combined with the transition to renewable energy sources. These efforts are linked intrinsically to meeting net-zero emissions goals.
- 45% of respondents report having announced formal net-zero goals.
- 30% aim to hit net zero by 2030.
Digital tech, employee training play a role: Also on the rise is the number of companies that recognize the importance of digital solutions in their sustainability efforts.
- These tools are being used to manage and monitor materials and energy consumption, optimize operations to improve efficiency and report sustainability progress.
- Respondents also say meeting sustainability targets must include engaging employees through education and training, as well as greening their supply chain.
The last word: An overwhelming 90% of all respondents agree that manufacturing has a special responsibility to society to become more sustainable and accelerate the transition to a future circular industrial economy.
Interested in putting some renewable energy solutions into action, including solar power, battery storage and LED lighting? Programs from utility companies and other entities enable efficiency upgrades with little or no upfront capital. Connect with NAM Energy to explore your options!
How a Manufacturer Uses R&D to Keep Old Jets Flying

What does the U.S. military do when an expensive asset like a plane or a weapons system begins to break down?
Often, it turns to companies like Parts Life, Inc.—an innovative manufacturer that can reverse-engineer obsolete parts and help find solutions for hard-to-replicate products. But after a tax law change went into effect in 2022, the New Jersey–based manufacturer is facing increased costs for research and development, creating a barrier to the kind of innovation that is the focus of its business.
The change: Until the beginning of 2022, businesses could deduct 100% of their R&D expenses in the same year they incurred the expenses. Starting this year, however, a tax law change requires businesses to spread their deductions out over a period of five years, making it more expensive to invest in growth and innovation.
A focus on innovation: For Parts Life, coming up with new ideas is an essential, daily activity.
- “Parts Life is built around being a solutions provider,” said Parts Life President and CEO Sam Thevanayagam. “We are providing solutions for very expensive and mission-critical assets that are extremely strategic for the defense of the nation, but are also older—so their parts are not necessarily being supported.”
- “That’s where we come in to do reverse engineering. So, we’re looking at an old problem, but using innovation to solve it going forward.”
A benefit for savings: By helping the military extend the life of its assets, Parts Life also helps taxpayers.
- “We’re taking care of the warfighter and the taxpayer,” as Thevanayagam puts it.
A look ahead: As global conflicts shift, the U.S. military needs suppliers like Parts Life to help it develop solutions for future challenges, too.
- “Right now, our military is coming out of conflicts in Afghanistan and Iraq, but future conflicts may involve different terrain with different problem sets,” said Thevanayagam.
- “The work that we are doing today is helping them figure out how to approach those challenges. We’re having them tell us where they need to be, and then we’re helping them with the innovation they need to be successful.”
A tough choice: With the change in tax law, companies like Parts Life will be forced to make difficult decisions about how to spend scarcer resources, harming their ability to do critical, forward-looking work.
- “Currently, we’re leaning forward in resources and talent to lead the future,” said Thevanayagam. “If the government is going to pull the rug out from under us, we’re not going to be able to be aggressive. We’ll have to focus on maintaining our business rather than investing in new innovation.”
Our take: The NAM has pushed forcefully for the tax change to be reversed—and in October, told policymakers that the R&D amortization provision poses a “serious threat to our national security,” in part because of its impact on manufacturers like Parts Life that supply and support the U.S. military.
The bottom line: “The only way for us to continue to be relevant is to make sure that we’re investing in innovation and seeing what we can do to be a part of designing the future,” said Thevanayagam.
Visit the NAM’s R&D Action Center for critical R&D policy updates, industry stories and an opportunity to engage directly with your members of Congress.
Why Manufacturers Need R&D Tax Certainty

This story can also be found within the NAM’s R&D action center.
For companies like O-I Glass, Inc.—a glass manufacturing company headquartered in Perrysburg, Ohio—research and development just got a lot more expensive.
Until the beginning of 2022, businesses including manufacturers could deduct 100% of their R&D expenses in the same year they incurred the expenses—but a change in the tax law that took effect this year required businesses to spread deductions over a five-year timeframe. O-I Vice President of Global Tax and Business Services Scott Gedris explained how that impacts the company.
The scale: With 17 plants in 13 states around the country—and 70 plants in 19 countries around the world—O-I has a significant reach, serving both large multinational companies and smaller customers like microbrewers and small batch spirits manufacturers.
- The scale of the operation means that O-I invests significantly in R&D, working to develop innovative processes and specific product designs to meet individual customer needs.
- “If you look at our public financial statements, we spent $82 million in 2021 on R&D—primarily in the U.S.—and that is a significant investment for us,” said Gedris.
Case in point: In the past decade, O-I has invested heavily in developing more effective, efficient and sustainable processes. In 2011, it built a 24,000-square-foot R&D facility on its Perrysburg, Ohio, campus and has announced plans for a new glass manufacturing facility in Bowling Green, Kentucky, using technology developed at the Ohio facility.
- Because the company spends so much of its resources on R&D, a significant increase in the cost of investment would require it to make difficult decisions.
- “Anything that comes out of this in terms of tax dollars … creates a choice within our organization about where we allocate our capital,” said Gedris.
Environmental effects: At a time when O-I is making important investments in sustainability, a significant reduction in available resources could present obstacles to the company’s environmental goals.
- “When we rebuild a glass manufacturing furnace, that is a multimillion-dollar investment. The cost continues to increase with inflation and investment in modern technology that we need in order to meet our corporate sustainability goals,” said Gedris.
- “With the cost of that equipment increasing, if we’ve got $10 million less because of increased taxes, we need to evaluate whether we are going to rebuild a glass furnace in one of our 17 U.S. plants, or are we going to defer that? Alternatively, those dollars could come out of our R&D spend, which will impact what we are able to invest in future technology improvements.”
Human impact: Investments in innovation and R&D don’t just create better products and processes for consumers; they also support local economies across the country.
- “When we invest in a glass manufacturing furnace in these towns, it’s an investment in the community,” said Gedris. “We’ve got multigenerational glass manufacturers in those facilities. It’s a project that people depend on, and they have a lot of pride in the product and the processes at their facility.”
The last word: “When you’re investing in R&D, you’re investing long term—and that means you need certainty in the tax policy,” said Gedris.
Visit the NAM’s R&D Action Center for critical R&D policy updates, industry stories and an opportunity to engage directly with your members of Congress.
How Manufacturers Can Boost Their D&I Efforts
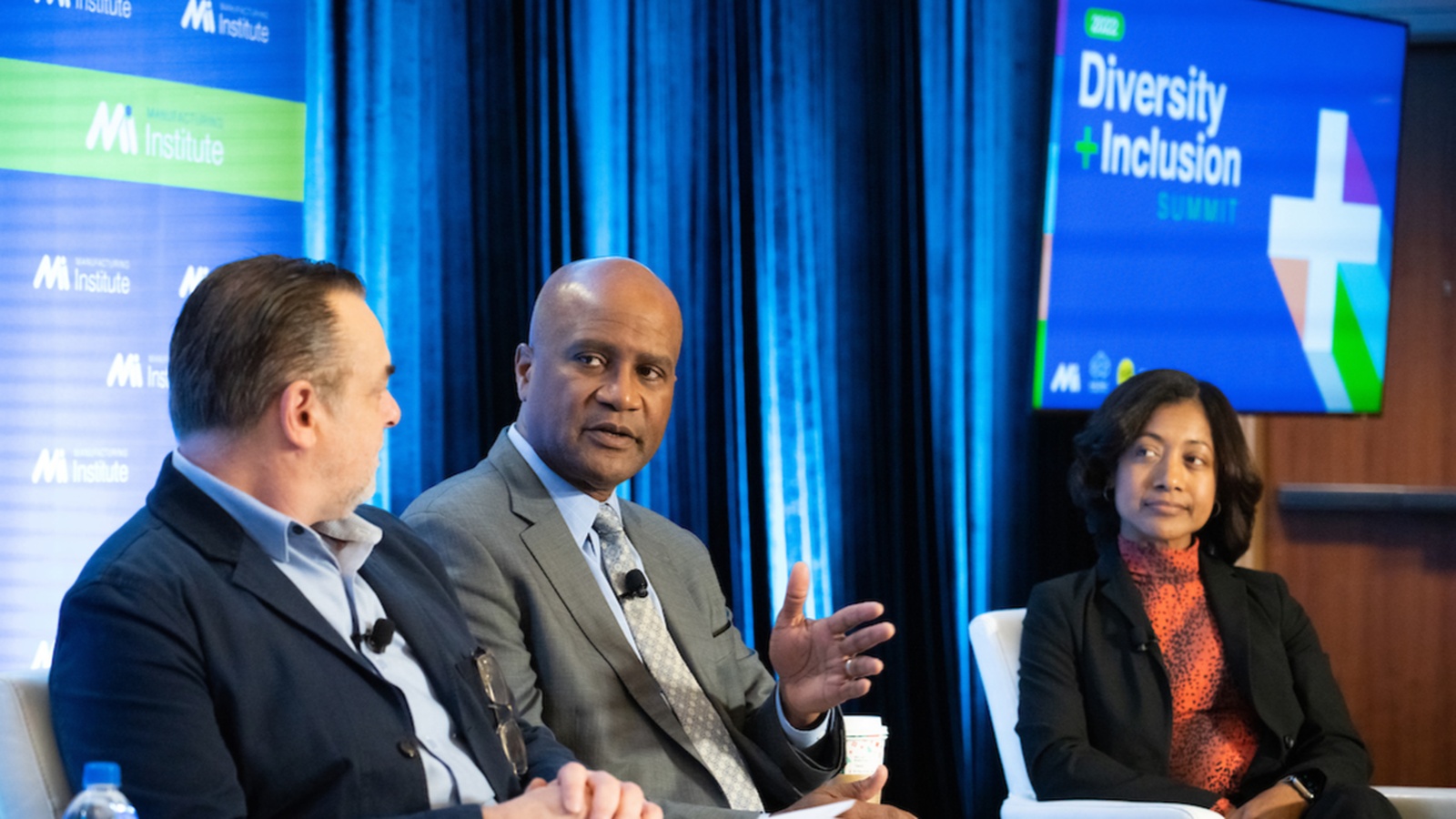

The manufacturing leaders who met in Washington, D.C., this month agreed wholeheartedly: D&I is integral to building and retaining the workforce of tomorrow.
At the third-annual Diversity+Inclusion Summit convened by the Manufacturing Institute, leaders gathered to share data, insights and lessons gleaned from their own D&I efforts. Hailing from many different industry sectors and companies of all sizes, the panelists and attendees laid out concrete actions that can transform companies’ D&I objectives.
Why it matters: With 2.1 million jobs expected to go unfilled in the industry by 2030, manufacturers need to find new populations of potential employees. Recruiting more women, racial and ethnic minorities and neurodiverse workers can expand companies’ talent pools and strengthen their workforces.
- In fact, increasing the current female workforce from 29% to 35% would fill the industry’s 746,000 open jobs all on its own, according to a recent study by the MI and Colonial Life.
- That’s why the MI is working to meet this target through its 35 x 30 Campaign—i.e., increasing the percentage of women in manufacturing to 35% by 2030.
How to do it: The summit offered important tips to help companies boost their D&I efforts, including:
- Get buy-in from company leaders: Research shows that D&I efforts lead to greater productivity, increased innovation and higher revenue—not to mention the recruitment and retention benefits. Once companies set D&I goals, leaders should incorporate D&I objectives into their annual goals to create opportunities for accountability.
- Use employee resource groups in a structured way: Companies should set up organizational structures for their ERGs that will ensure longevity and encourage fresh thinking, as well as align with companies’ overall D&I goals. These groups should have their own budgets and rotating leadership positions. When possible, the contributions of ERG leaders should be included in their incentive programs or annual goals.
- Educate your first-line supervisors about D&I: By training first-line supervisors on the latest in D&I and company-specific objectives, companies can help them both support their teams better and collect feedback to inform the overall effort.
- Offer child care and flexibility: In the post-pandemic environment, companies are still exploring what works best for them, but one thing is clear: to recruit and retain talent in a tight labor market, companies need to provide employees with options. (Check out our recent webinar on the same subject.)
Learn more: Interested in joining the conversation? Check out the MI’s D&I tools and resources, and register for upcoming events, including our upcoming Virtual Diversity+Inclusion Summit on Dec. 16, here. The virtual summit will include some recorded sessions from this event as well.
Rail Unions Move Closer to National Strike

Another large labor union has voted to reject the rail deal brokered in part by the Biden administration, moving the industry closer to a strike, according to CNBC.
Split decision: Two of the largest railroad labor unions in the United States went separate ways during their contract ratification votes, which were announced on Monday. The Sheet Metal, Air, Rail and Transportation Workers – Transportation Division voted against the proposed agreement by a slim margin, while the Brotherhood of Locomotive Engineers and Trainmen voted to ratify it.
What it means: This latest action raises the likelihood of a rail work stoppage in early December. In total, 8 of 12 unions have now ratified the tentative agreement concluded in September while the rank-and-file membership of 4 unions have rejected it.
- Should one union choose to go on strike, the broad impact would cripple the national freight rail network.
The impact: The railroad industry and major shipping groups have found that a strike would likely cost around $2 billion per day, also according to CNBC. It would affect every major rail operator.
- “The American Chemistry Council, which represents companies including 3M, Dow, Dupont, BP, Exxon Mobil and Eli Lilly, said a rail strike would impact approximately $2.8 billion in chemicals cargo a week, and lead to a GDP decline and renewed inflation.”
- “Other industries, from agriculture to retail, have warned of the economic risks of a strike.”
Next steps: Negotiations will continue through a cooling-off period that runs until early December. If a deal is not reached by 12:01 a.m. EST on Dec. 5, a strike could occur. The NAM and others have urged Congress to take action under the Railway Labor Act and pass legislation that would avert a strike if railroads and rail unions cannot reach such a deal.
What we’re saying: “Manufacturers are disheartened by today’s news on the further unraveling of rail negotiations,” said NAM President and CEO Jay Timmons. “It’s clear that Congress, both Democrats and Republicans, must be prepared to work together immediately to avert a rail strike and prevent further damage to our supply chain.”
“Cybersecurity Finds You”: An Interview with Rockwell Automation’s CISO

When asked how she got into cybersecurity, Nicole Darden Ford replies “cybersecurity kind of finds you.” The new chief information security officer at Rockwell Automation began her career in the military, where she first got into cybersecurity, then created a cybersecurity program for the U.S. Department of Agriculture before taking several leadership roles in the private sector.
Today, her advice for companies is surprisingly similar: cyberattacks will find you. As she puts it, “It’s not if, it’s when. And it’s not one time, it’s several.”
So how should manufacturers prepare for these threats? We spoke to Darden Ford recently about her recommendations, as well as Rockwell’s efforts to safeguard its own supply chain and provide services to other companies.
The current situation: “Manufacturers account for 65% of industrial ransomware last year. We’ve seen an unprecedented number of attacks, and we’ve seen attackers focus on OT,” Darden Ford says. She predicts the attacks on OT will only escalate.
- Meanwhile, many manufacturers have a clear strategy for IT, but they have not given as much thought to protecting their operational technology. Yet, as machines get more connected, their operations may become more vulnerable—especially as companies try to integrate legacy systems that weren’t “meant to be connected or patched.”
- In addition, “because we are so connected, there are third-party risks,” Darden Ford says. Small manufacturers may be more inviting targets for hackers than they realize, since their systems could provide a back door into the networks of their larger clients.
- On the plus side, manufacturers are getting smarter in building their defenses, she says. And that’s where Rockwell comes in.
Rockwell’s role: Rockwell aspires to become a “trusted advisor” to companies seeking cyber defenses, says Darden Ford. It already manufactured OT, so moving into cybersecurity for such equipment was a natural next step.
- Its partnerships with other firms, including Dragos, CrowdStrike, Cisco and others, allows
 Rockwell to offer bespoke cyber monitoring and other services to its clients.
Rockwell to offer bespoke cyber monitoring and other services to its clients. - These services include penetration testing, threat detection and response and an OT “SOC”—i.e., a security operations center, which monitors threats to clients’ operations remotely.
How it works: “We have an OT cybersecurity roadmap—it starts with an assessment in your specific OT space, then walks through potential risks,” Darden Ford says. (See the end of this article for her detailed description of this roadmap.)
- The process includes building an “asset inventory, as you can’t protect what you don’t know.”
- “Then we talk about ways you can reduce your attack surface,” Darden Ford continues. “This is about segmentation. We help organizations divide their network into different domains. If you have ransomware or malware that propagates very quickly, then you have the opportunity to quarantine it.”
- In addition, the roadmap helps companies decide which tools and resources to use. For OT, you need to use very passive systems that don’t interfere with “getting the product out the door,” Darden Ford says.
After this process is complete, Rockwell’s SOC helps clients stay safe and hone their responses to real attacks.
- The SOC keeps eyes on a company’s operations remotely, notifies it of breaches within the plant network and helps it decide which threats to tackle. As Darden Ford says, the SOC stands in for the teams that companies would otherwise have to hire themselves.
On-site resources: Manufacturers can tap their existing staff to work on cyber defenses, including with offsite monitors. Darden Ford recommends drafting “the plant engineering team, along with the IT team,” who would have the knowledge and resources required.
A community effort: Large manufacturers should help educate small manufacturers on cyber issues, says Darden Ford.
- “We have a lot of suppliers, so to mitigate third-party risk, we provide more awareness about OT and advice about upping their cyber hygiene. We work closely with suppliers and do a lot of knowledge sharing,” she says.
Collaboration at the top: In addition, it’s also beneficial for CISOs and manufacturing leaders to consult their peers in what Darden Ford calls “mastermind sessions.”
- These conversations have provided her with “a lot of insights and data,” she says. She gets indispensable input on “strategies, frameworks, journeys and roadmaps,” as companies try to find their way through this cyber landscape together.
The bottom line: When asked what she says to companies that doubt the need for cyber protections, Darden Ford has a simple answer: “You wouldn’t drive your car without insurance—that’s what this is.”
- “What used to be optional is becoming mandatory,” she adds. “For small or midsize companies, you are still going to have to report” back to your large customers, many of whom require stringent protections of their suppliers. Those requirements will only get “more and more rigorous over time,” she warns.
- In other words, however you choose to do it, “you need a plan.”
The Roadmap
Darden Ford supplied us with her account of Rockwell’s cyber roadmap for its own suppliers, below. “The playbook aligns with the NIST framework, showing you step-by-step how to audit your current security state, identify gaps and take a proactive approach to mitigate risk,” she says. Here is her account of the key steps.
Step #1: Discover
- Know where you stand. Conduct a security and risk assessment—log all issues and review progress against findings.
- You can’t protect what you can’t see. You must gain a full understanding of what network assets you have on your plant floor and their current state. Start by conducting extensive network discovery and asset inventory.
Step #2: Remediate
- Work with stakeholders to prioritize assets and organizational risk levels. Take the necessary steps to eliminate, upgrade or replace unneeded, unused or unsupported OT applications and infrastructure. This will look different for every organization based on what you discover in Step #1.
Step #3: Isolate
- Establish a perimeter by physically and logically segmenting your networks. Put up a firewall and establish internal and external cybersecurity policies to protect your OT assets. Set up an on-premises industrial data center to encapsulate critical applications inside the protected OT network.
- Secure endpoints with security software on plant floor assets.
- Enable third-party remote access. Third parties need access, but you must control the access and maintain visibility into what they’re doing in your network by enabling OT access controls.
Step #4: Monitor and Respond
- Now that you have a solid foundation in place, the next step is to implement OT network monitoring to provide real-time OT cybersecurity, including malicious event/asset risk alerting, network diagnostics, AI learning and KPI dashboarding. The data only works for you if you are continuously viewing and reacting to it.
- Establish an OT SOC for 24/7 real-time alert monitoring, acknowledgement and triage. Cyberattacks aren’t limited to 9–5.
- Create an integrated IT/OT cyber event response team. Define event response and isolation protocols. IT/OT must have equal involvement and buy-in for these protocols to be successful. Execute tabletop exercises to simulate attacks and outcomes.
How Managers Can Produce Top-Notch R&D

As innovation in manufacturing continues at breakneck speed, research and development is more important than ever—but it requires outstanding managers to make it all happen.
So how do these managers get the education and insights they need? The Innovation Research Interchange, a network of cross-industry innovators that the NAM combined with earlier this year, has an answer: an executive management course called Shaping Innovation Leaders.
The gist: Co-hosted by the Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University, the course provides a forum for strategic thinking, education and networking for technology leaders from around the world.
- In 2023, it will take place on May 13–19 on the Northwestern campus in Evanston, Illinois.
The details: The goal of this seven-day program is to develop midlevel managers into leaders for their companies, by covering topics including:
- Evaluating financial results;
- Segmentation, targeting and positioning;
- Growing and defending your brand;
- Legal and strategic investments;
- Building a better network; and
- Negotiating skills and strategic alliances;
Who’s involved: To get a sense of this event’s caliber, look no further than the attendees from the 2022 course.
- They hailed from a wide range of companies, including manufacturers such as Mars, Procter & Gamble, John Deere, Hershey, NatureWorks, Air Liquide, Kimberly-Clark Corporation, Sherwin-Williams and many, many more.
The reviews are in: Participants in the 2022 course were enthusiastic about what they learned and experienced.
- “[I’m] really super impressed with the program, soup to nuts,” said John Deere Manager for Global Strategic Communications & Culture Jacqueline Kiple. “One of my favorite aspects of the program was really getting a chance to think about our business a little bit differently … to take a step back and think about the higher-level impacts that affect decision-making in our respective organizations.”
- “What I really enjoyed about this course was first and foremost the esteemed professors. … [The course] gives you a really big view of all the information you need to really understand business and understand the decisions that are getting made,” said Sherwin-Williams Associate R&D Director Tony Rook. “It gives you that top-level view of how you add value to [your] organization.”
Get involved: Registration is now open for the 2023 course. You can find additional information and register here.
Concrete Mixer Maker Finds a Growth Formula
Even amid so much economic uncertainty, Cemen Tech is on track for a year of unprecedented growth. Leaders of the company, the world’s largest manufacturer of volumetric technology, attribute a good deal of its success to its loyal workforce.
Allegiance creator: Just what contributes to that worker loyalty? The answer may well be Cemen Tech’s unusual generosity.
- “We considered a number of new and different ways to continue to attract and retain good people,” Cemen Tech President and CEO Connor Deering said. “In September 2021, we made the decision to cover 100% of employee health insurance costs, the net effect of which is essentially our folks taking home more of the money they earn. That has really helped with retention.”
- The Indianola, Iowa–based company also raised wages across the board and began offering employees season tickets for local sports teams.
A new approach: Full health insurance coverage made a difference when it came to attracting and keeping workers, but the volumetric concrete mixer manufacturer was still hitting another roadblock when it came to employment: finding people with the right qualifications. So, it set out to solve the problem in house.
- As part of a planned facility expansion, the company is setting aside space for the new “Cemen Tech University,” an innovative answer to the question of how to develop employees with highly desired, specialized skills. Classes are tentatively set to start in January 2023.
- The company is also working with area high schools and technical schools to forge partnerships in which students work for Cemen Tech part time, while still pursuing their diplomas or degrees.
- “This way, we train applicants for immediate success on the job, helping to ensure a strong fit between the employee and the company from the start,” Deering said. “It also gives us an opportunity to teach new hires about our organizational culture. … I believe [our education efforts] will help support an educated team member who’s connected to our culture, resulting in a happier, better and more long-term employee.”
More incentives: Last March, Cemen Tech found a way to boost shift-worker attendance with a points-based rewards system.
- “We implemented an attendance bonus—if an employee stays within a certain number of points [for coming to work], they can earn an additional $90 a week,” said Cemen Tech Director of Human Resources Emily Lyons. “We have seen that help in terms of attracting and retaining employees and further incentivizing employees to achieve consistent attendance.”
- The company has also increased the referral bonus given to existing employees who bring in new hires, Lyons said.
Advice: Manufacturers looking to see similar growth to Cemen Tech, which is set to expand 65% this year, should consider implementing some of the firm’s ideas (if financially feasible). But companies should be prepared to incur some financial cost along the way.
- “Our growth has helped offset the profitability loss [from the increased benefits], but the reality is that our business is people,” Deering said. “If we don’t have people—good people—we’re not going anywhere. So, the fact that we’re little less profitable at the moment is OK, as long as we can continue to grow.”
Manufacturers Renew Call for Action on Immigration
NAM CEO says broken system is harming manufacturers’ competitiveness
Washington, D.C. – National Association of Manufacturers President and CEO Jay Timmons addressed the Minnesota Chamber of Commerce’s Manufacturers’ Summit today, where he made another call for policymakers to act on immigration, saying it is time to “fix this problem now.” Timmons called on Congress to act in the year-end government funding bill. His remarks come as the NAM rereleased its immigration proposal “A Way Forward.”
Excerpts from Timmons’ speech:
“First and foremost, this is a humanitarian issue. We see it play out in tragic ways—including family separations at the border and confusion as families seek to reunite following a harrowing journey.”
“But as manufacturing and business leaders, we also know there are serious economic consequences. Research and development—the cornerstone of innovation and our industry’s success—depends on access to the best and brightest from across the world.”
“The broken immigration status quo is also preventing us from growing our talent pool, leaving jobs unfilled. There are around six job seekers for every 10 job openings in the U.S., and our population growth is slowing. Last year, the U.S. population grew at its slowest rate ever.”
“Last year’s infrastructure law and this year’s CHIPS and Science Act prove that Congress can still get bipartisan things done—and immigration should be next on the list, whether it’s one bill or multiple bills. We would absolutely support a long-term, comprehensive legislative fix that addresses all of these issues, but we also want to be realists. We have a workforce crisis that needs to be addressed now, so let’s take action where we can. We want to focus on the art of the possible. One approach would be to address some of these issues in the year-end government funding bill.”
First released in 2019 and updated to reflect current challenges, the NAM’s “A Way Forward” proposal identifies seven core areas of action for Congress and the administration to take:
- Strengthen border security through physical infrastructure and best-in-class technology.
- Prioritize America’s workforce needs through reforms to the legal immigration system.
- Reform nonimmigrant visas and temporary worker programs to reflect employer needs, including a fund to support STEM programs so that we can reduce the need for these types of visas in the future.
- Provide a permanent and compassionate solution for populations facing uncertainty, including the Dreamers, who were brought here as children and know no other home.
- Reform asylum and refugee programs for a more orderly and humane system, including asylum standards consistent with our values.
- Fix the problem of the unauthorized population with a firm reset, requiring an orderly process of review, including financial penalties for those who seek to become legal and deportation for those who choose to stay in the shadows.
- Strengthen the rule of law so that it is respected and followed by all, with a focus on gang violence and also on requiring localities to cooperate to advance the enforcement of immigration priorities.
View “A Way Forward” in full here.
-NAM-
The National Association of Manufacturers is the largest manufacturing association in the United States, representing small and large manufacturers in every industrial sector and in all 50 states. Manufacturing employs more than 12.8 million men and women, contributes $2.77 trillion to the U.S. economy annually and accounts for 58% of private-sector research and development. The NAM is the powerful voice of the manufacturing community and the leading advocate for a policy agenda that helps manufacturers compete in the global economy and create jobs across the United States. For more information about the NAM or to follow us on Twitter and Facebook, please visit www.nam.org
New NAM Board Members to Bolster Manufacturing Competitiveness

The NAM is constantly working to support and strengthen the men and women who make things in America. That mission is upheld by outstanding members of the NAM Board of Directors and their commitment to promoting the industry’s competitiveness on the global stage—a goal laid out in the NAM’s “Competing to Win” agenda.
Welcoming new faces: A number of new members have been elected to the board and will begin their two-year terms in January. They come from many sectors of the industry and companies both large and small, holding an array of leadership roles and boasting a wide range of experience. All of them are dedicated to ensuring that manufacturers in the U.S. have the tools they need to prosper.
The new members include the following:
- Edward Blair, president, Lutron Electronics Co., Inc.
- Sara Beth Burton, senior vice president, global supply chain, Hallmark Cards, Inc.
- Richard Cammarano, president and chief executive officer, Tech-Etch, Incorporated
- Karl Ehemann, vice president, global manufacturing and quality, Corning Incorporated
- Ed Elkins, executive vice president and chief marketing officer, Norfolk Southern Corporation
- Cynthia Farrer, senior vice president, global operations and integrated supply chain, Allegion plc
- Aimee Gregg, vice president and general manager, containerboard and recycling, International Paper
- John Hartner, founder, Digital Industrialist LLC
- Christopher Kastner, president and chief executive officer, Huntington Ingalls Industries
- Ram Krishnan, executive vice president and chief operating officer, Emerson
- Reece Kurtenbach, chief executive officer and president, Daktronics, Inc.
- Rose Lee, president and chief executive officer, Cornerstone Building Brands
- Thomas Long, co-chief executive officer, Energy Transfer LP
- Michael McGarry, chairman and chief executive officer, PPG
- Lori Miles-Olund, president, Miles Fiberglass & Composites, Inc.
- Christopher Perkins, president North America and senior vice president Taste & Beyond North America, Firmenich, Inc.
- Kimberly Ryan, president and chief executive officer, Hillenbrand, Inc.
- Karin Shanahan, executive vice president, global product development and supply, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Matt Shields, senior vice president, global animal health manufacturing, Merck & Co., Inc.
- Sachin Shivaram, chief executive officer, Wisconsin Aluminum Foundry
- Shruti Singhal, chief executive officer, Chroma Color Corporation
- Mark Smucker, president and chief executive officer, The J.M. Smucker Company
- Matt Wood, national industry leader, commercial products practice, FORVIS
- Brent Yeagy, president and chief executive officer, Wabash
- Renée Zemljak, executive vice president, midstream, marketing & fundamentals, Ovintiv USA Inc.
What we’re saying: “The diverse backgrounds of our new board members, and their varied experience across many manufacturing sectors, make their counsel invaluable to the NAM in its efforts to bolster the industry’s competitiveness,” said NAM Chief of Staff Alyssa Shooshan. “We are counting on their insights and dedication to help steer manufacturers through this turbulent time and into a position of even greater strength.”
